| [1] |
LIU D S, WEI G M, LI T C, et al. Effects of alkaline pretreatments and acid extraction conditions on the acid-soluble collagen from grass carp ( Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,172:836−843. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.147
|
| [2] |
徐逍, 徐卉, 陶宁萍. 暗纹东方鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白的提取工艺优化及其功能特性[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(10):168−176
XU X, XU H, TAO N P. Optimization of preparation process of collagen from Takifugu obscurus skin and its functional properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(10):168−176.
|
| [3] |
SUBHAN F, HUSSAIN Z, TAUSEEF I, et al. A review on recent advances and applications of fish collagen[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2021,61(6):1027−1037. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1751585
|
| [4] |
AHMED M, VERMA A K, PATEL R. Collagen extraction and recent biological activities of collagen peptides derived from sea-food waste: A review[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy,2020,18:100315. doi: 10.1016/j.scp.2020.100315
|
| [5] |
YAN M Y, JIANG X J, WANG G C, et al. Preparation of self-assembled collagen fibrillar gel from tilapia skin and its formation in presence of acidic polysaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,233:115831. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115831
|
| [6] |
王丹, 吴反修, 宋丹丹等. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2022:21−38
WANG D, WU F X, SONG D D, et al. China fishery statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2022:21−38.
|
| [7] |
BHUIMBAR M V, BHAGWAT P K, DANDGE P B. Extraction and characterization of acid soluble collagen from fish waste:Development of collagen-chitosan blend as food packaging film[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2019,7(2):102983. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.102983
|
| [8] |
CHEN J D, LI L, YI R Z, et al. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2016,66:453−459. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.10.070
|
| [9] |
CHUAYCHAN S, BENJAKUL S, KISHIMURA H. Characteristics of acid-and pepsin-soluble collagens from scale of seabass ( Lates calcarifer)[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,63(1):71−76. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.03.002
|
| [10] |
曾少葵. 罗非鱼鱼皮胶原蛋白的提取及其功能特性的研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2007
ZENG S K. Study on isolation and characterization of collagens from the skin of Oreochromis niloticus[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China, 2007.
|
| [11] |
SKIERKA E, SADOWSKA M. The influence of different acids and pepsin on the extractability of collagen from the skin of Baltic cod ( Gadus morhua)[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,105(3):1302−1306. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.04.030
|
| [12] |
SHI L F, TIAN H H, WANG Y X, et al. Effect of pH on properties of golden pompano skin collagen-based fibril gels by self-assembly in vitro[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(13):4801−4807. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10539
|
| [13] |
JOHNY L C, KUDRE T G, PV S. Acid and pepsin soluble collagens from skin by-product of red-bellied pacu ( Piaractus brachypomus): Extraction and comparative characterizations towards finding substitute to bovine and porcine collagen[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,2021,30(3):364−376. doi: 10.1080/10498850.2021.1884374
|
| [14] |
MENG D W, LI W, URA K, et al. Effects of phosphate ion concentration on in-vitro fibrillogenesis of sturgeon type I collagen[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,148:182−191. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.128
|
| [15] |
寇慧芝, 张惠惠, 韩庆秋, 等. 氨基酸组成对胶原与整合素 α2 β1结合能力的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(6):143−150
KOU H Z, ZHANG H H, HAN Q Q, et al. Effects of amino acid composition on the binding ability of collagen to integrin α2 β1[J]. Food Science,2023,44(6):143−150.
|
| [16] |
冯玲玲, 冯进, 李春阳. 海蜇Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的提取及结构特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(7):15−21
FENG L L, FENG J, LI C Y. Extraction and structural characteristics of type I collagen from Rhopilema esculenta[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(7):15−21.
|
| [17] |
郑清瑶, 曹文红, 韩昱梁, 等. 几种提取方法制备的糙刺参体壁胶原蛋白的特性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(15):145−152
ZHENG Q Y, CAO W H, HAN Y L, et al. Characteristics of collagens from the body wall of Stichopus horrens prepared by several extraction methods[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(15):145−152.
|
| [18] |
LIU D S, ZHOU P, LI T C, et al. Comparison of acid-soluble collagens from the skins and scales of four carp species[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2014,41:290−297. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.04.030
|
| [19] |
TANG L L, CHEN S L, SU W J, et al. Physicochemical properties and film-forming ability of fish skin collagen extracted from different freshwater species[J]. Process Biochemistry,2015,50(1):148−155. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2014.10.015
|
| [20] |
BI C H, LI X H, XIN Q, et al. Effect of extraction methods on the preparation of electrospun/electrosprayed microstructures of tilapia skin collagen[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2019,128(2):234−240. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.02.004
|
| [21] |
NIU L H, ZHOU X, YUAN C Q, et al. Characterization of tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus) skin gelatin extracted with alkaline and different acid pretreatments[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,33(2):336−341. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.04.014
|
| [22] |
GÓMEZ-GUILOEN M C, MONTERO P. Extraction of gelatin from megrim ( Lepidorhombus boscii) skins with several organic acids[J]. Journal of Food Science,2001,66(2):213−216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2001.tb11319.x
|
| [23] |
CHENG F Y, HSU F W, CHANG H S, et al. Effect of different acids on the extraction of pepsin-solubilised collagen containing melanin from silky fowl feet[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,113(2):563−567. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.08.043
|
| [24] |
RAN Y Q, SU W, MA L, et al. Insight into the effect of sulfonated chitosan on the structure, rheology and fibrillogenesis of collagen[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,166:1480−1490. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.027
|
| [25] |
周瑞, 李若男, 周丽莎, 等. 暗纹东方鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白的提取及其特性[J]. 水产学报,2020,44(8):1349−1359
ZHOU R, LI R N, ZHOU L S, et al. Extraction and characteristics of collagens from the skin of puffer fish ( Tetrodontiformes fasciatus)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2020,44(8):1349−1359.
|
| [26] |
汤俊, 魏东芝, 张国钧, 等. 胶原蛋白的高效制备及与明胶的鉴别[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(7):54−60
TANG J, WEI D Z, ZHANG G J, et al. Development of efficient preparation and identification methods for bovine collagen[J]. Food Science,2010,31(7):54−60.
|
| [27] |
FERRARO V, GAILLARD-MARTINIE B, SAYD T, et al. Collagen type I from bovine bone. Effect of animal age, bone anatomy and drying methodology on extraction yield, self-assembly, thermal behaviour and electrokinetic potential[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,97:55−66. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.068
|
| [28] |
张金伟, 曹念, 陈武勇. 微波辐照对胶原蛋白三股螺旋结构的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2018,38(5):1353−1357
ZHANG J W, CAO N, CHEN W Y. Influence of microwave iradiation on colagen triple helix structure[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2018,38(5):1353−1357.
|
| [29] |
GUO M H, LIU S C, ISMAIL M, et al. Changes in the myosin secondary structure and shrimp surimi gel strength induced by dense phase carbon dioxide[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,227:219−226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.050
|
| [30] |
HE L, YANG J, XU C Z, et al. Effect of pre-shearing treatment on the molecular structure, fibrillogenesis behavior and gel properties of collagen[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2020,44(17):6760−6770. doi: 10.1039/D0NJ00054J
|
| [31] |
NIKOO M, BENJAKUL S, BASHARI M, et al. Physicochemical properties of skin gelatin from farmed Amur sturgeon ( Acipenser schrenckii) as influenced by acid pretreatment[J]. Food Bioscience,2014,5:19−26. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2013.10.004
|
| [32] |
LIU D S, LI L, REGENSTEIN J M, et al. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp ( Hypophthalmi chthys nobilis)[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,133(4):1441−1448. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.032
|
| [33] |
SINTHUSAMRAN S, BENJAKUL S, KISHIMURA H. Comparative study on molecular characteristics of acid soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of seabass ( Lates calcarifer)[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,138(4):2435−2441. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.136
|
| [34] |
MUYONGA J H, COLE C G B, DUODU K G. Characterisation of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult Nile perch ( Lates niloticus)[J]. Food Chemistry,2004,85(1):81−89. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.06.006
|
| [35] |
YAN M Y, QIN S, LI J. Study on the self-assembly property of type I collagen prepared from tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus) skin by different extraction methods[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2015,50(9):2088−2096.
|
| [36] |
SALVATORE L, GALLO N, AIELLO D, et al. An insight on type I collagen from horse tendon for the manufacture of implantable devices[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,154:291−306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.082
|
| [37] |
邓明霞, 汪海波, 杨玲, 等. 氨基酸组成及溶剂环境对淡水鱼胶原蛋白热稳定性能的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2015,31(12):111−120
DENG M X, WANG H B, YANG L, et al. Effects of amino acid composition and solvent environment on the thermal stability of fish collagen[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2015,31(12):111−120.
|
| [38] |
THUANTHONG M, SIRINUPONG N, YOURAVONG W. Triple helical structure of acid-soluble collagen derived from Nile tilapia skin as affected by extraction temperature[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2016,96(11):3795−3800. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7572
|






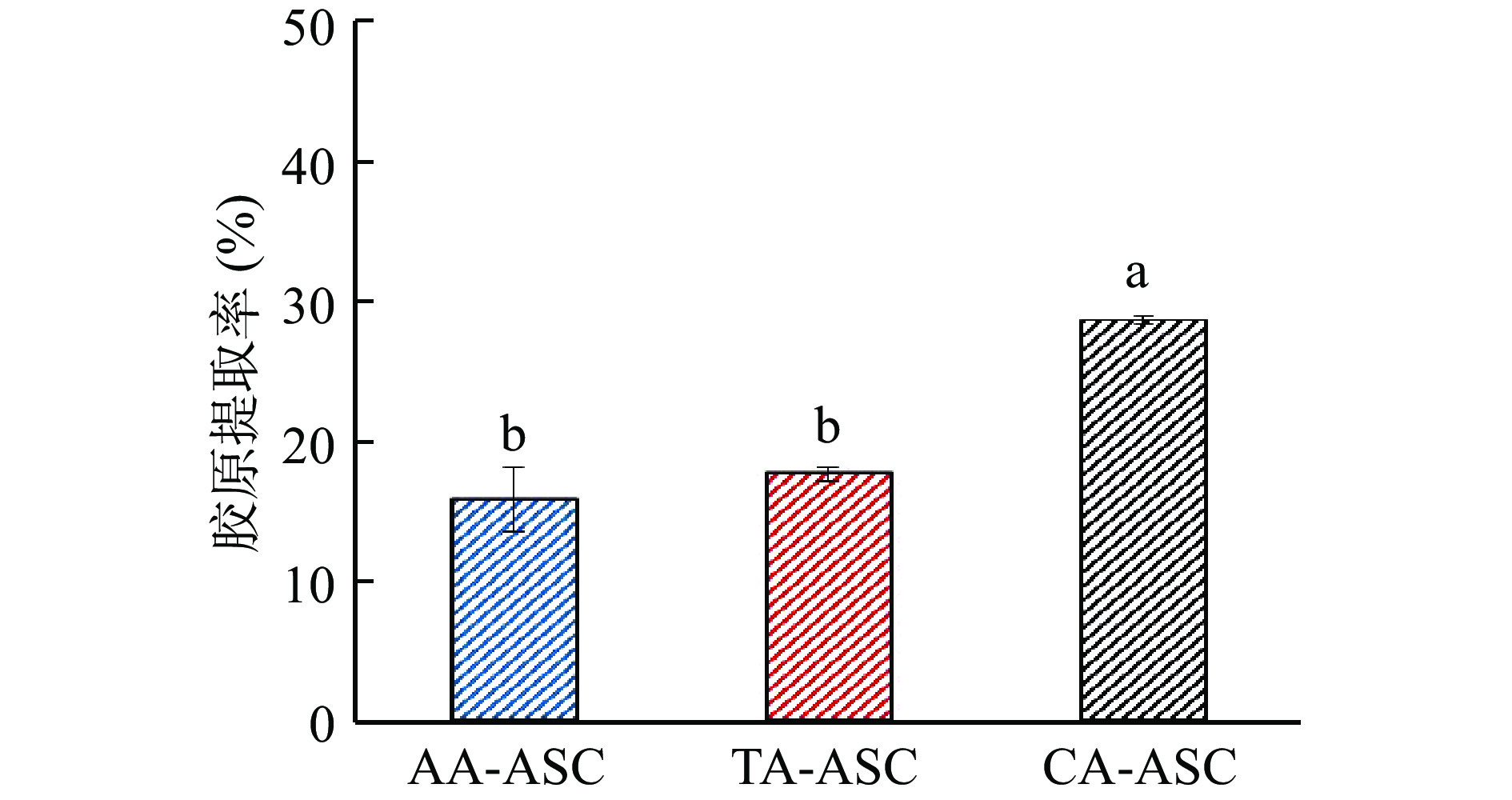

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: