Regulating Effect of Ginseng in Combination with Dandelion Root on Shanghuo Symptoms in Rats
-
摘要: 为改善食用人参出现的“上火”症状,提高人参的普适性,通过动物实验,分别设置正常组、2、4 g/kg人参组以及2、4 g/kg人参与蒲公英根配伍组进行灌胃19 d,测量体温、血压及血清中与“上火”相关联的5-羟色胺(5-HT)、促甲状腺激素(TSH)、皮质酮(CORT)等指标。结果表明,2、4 g/kg人参与蒲公英根配伍组体温及血压均低于人参组,其中4 g/kg配伍组效果更显著(P<0.05);与正常组比较,人参组5-HT含量下降,TSH、17-羟皮质类固醇(17-OHCS)、CORT、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)含量升高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);与人参组相比,2、4 g/kg人参与蒲公英根配伍组5-HT含量升高,TSH、17-OHCS、CORT、TNF-α含量下降,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。由此表明,利用人参与蒲公英根配伍可提高人参和蒲公英根价值,调节食用人参引起的“上火”症状。Abstract: In order to improve the symptoms of "Shanghuo" and the universality of ginseng, the animals randomly divided into control group, the 2 and 4 g/kg ginseng group and ginseng dandelion root compatibility group were given intragastric administration for 19 days, respectively. Body temperature, blood pressure and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), corticosterone (CORT) and other indicators associated with "Shanghuo" were measured. The results showed that the body temperature and blood pressure of the 2 and 4 g/kg groups were lower than those of the ginseng group, and the effect of the 4 g/kg group was more significant (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the content of 5-HT in ginseng group decreased, and the contents of TSH, 17-hydroxy corticosteroid (17-OHCS), CORT, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were significantly increased (P<0.05). Compared with ginseng group, the contents of 5-HT in the combination group of 2 and 4 g/kg ginseng and dandelion root compatibility group were increased, and the contents of TSH, 17-OHCS, CORT, TNF-α were significantly decreased (P<0.05). The results indicated that compatibility of ginseng and dandelion root could improve the value of ginseng and dandelion root, and regulate the symptoms of "Shanghuo" caused by ginseng consumption.
-
Keywords:
- ginseng /
- dandelion root /
- compatibility /
- "Shanghuo" /
- blood pressure
-
人参(Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer)是伞形目五加科属下的多年生草本植物,至今已有4000年的历史,被誉为“百草之王”[1]。研究表明,人参中已经分离鉴定40余种人参皂苷单体,含有蛋白质、多肽、胆碱、果胶、多种糖类及维生素等有效成分,人参具有改善血压、加速肿瘤细胞凋亡、提高机体免疫力,增强老年人的智力、记忆力等功能[2−3]。服用人参益处繁多,但仍有部分人群食用人参会出现“上火”的临床症状。一般表现为牙喉疼痛、口舌生疮、便秘、血压升高等症状[4−5]。中医配伍理论可将存在副作用的中药材通过与其他中药合理地搭配在一起,使用药更加安全、有效[6−7]。蒲公英(Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz.)别名为婆婆丁,味苦、甘,性寒,是一种多年生草本药食同源植物[8]。蒲公英全草富含蒲公英甾醇、黄酮、绿原酸、果胶等化合物,同时含有多种维生素与丰富的蛋白质及碳水化合物[9]。蒲公英根中富含蒲公英醇、胆碱、有机酸、葡萄糖等物质,可抑制真菌生长,具有抗肿瘤、清热解毒、消肿散结、利尿通淋的功效,有很好的保健食用价值[10]。
人参和蒲公英根有较为突出的应用价值,近年来,国内外学者对人参和蒲公英根的化学成分及药理作用等研究较为深入。赵婷等[11]从腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase,AMPK)能量代谢调节的角度,探讨红参引起上火的机制,结果表明,红参上火的大鼠模型能量代谢增强,与红参活化AMPK,上调下游能量代谢相关因子表达,加快三羧酸循环有关。Xu等[12]通过动物实验,结果表明,人参组和红参组小鼠眼分泌物较多,而唾液分泌较少,这两组的Na+-K+-ATP酶活性也显著升高,并认为这种酶的活性可能是服用人参“上火”的主要指标。经研究表明,蒲公英作用机理为清除自由基和抑制酪氨酸酶活性,同时其具有较好的体内外抗氧化活性[13−14],因此可以减少自身机体的损伤。临床应用上还有蒲公英-生麦芽-丝瓜络配伍主治急性乳腺炎,具有清热解毒、抑制泌乳、疏通乳络等作用;蒲公英-茵陈-柴胡配伍主治急性胆囊炎,具有利胆祛湿、清热解毒、理气通附等作用;蒲公英-苦参-白鲜皮配伍主治急性、亚急性湿疹,具有消风止痒、清热解毒、燥湿通络等作用[15]。虽然人参与蒲公英益处繁多且具有良好的生理功效,但依据中医配伍理论将其配伍研究甚少,缺乏科学验证。
人参参与机体物质的代谢,对机体体内血液运输系统有正面的药理作用;可改善机体内肠道菌群环境,调节人体免疫系统,提高人体免疫力;对脑及神经系统的健全有促进作用[3]。蒲公英其药理作用广泛,如提高机体免疫力,降血糖、抗菌、增强免疫力、抗肿瘤、护肝、延缓衰老等一系列作用,在食品药品及保健品等领域有着广泛的应用[8]。蒲公英根中生物活性含量最高,且蒲公英根价格低廉,资源丰富,但目前尚未有对人参与蒲公英根配伍是否有改善“上火”作用的相关报道,因此,本实验为改善食用人参后出现的“上火”症状,将中医配伍理论应用于食品,通过蒲公英根与人参进行配伍,提高人参的普适性,研究人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”症状的影响,对人参和蒲公英根的深度开发和综合利用具有积极作用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
人参 延边大阳参业有限公司;蒲公英根 延边野林森茸药品有限公司;5-羟色胺(5-Hydroxytryptamine,5-HT)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL13043)、促甲状腺激素(Thyroid Stimulating Hormone,TSH)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL11830)、17-羟皮质类固醇(17-HydroxyCorticoSteroid,17-OHCS)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL11045)、皮质酮(corticosterone,CORT)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL12455)、白细胞介素-2(Interleukin-2,IL-2)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL13429)、白细胞介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL20896)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor-α,TNF-α)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:JL13202) 上海江莱生物科技有限公司;去甲肾上腺素(Norepinephrine,NE)酶联免疫试剂盒(批号:RA20557) 上海酶联生物科技有限公司;SPF级SD大鼠,雄性60只,6周龄,体质量205±10 g 均由延边大学实验动物中心提供,实验动物使用许可证号:[SYXK(吉)2020-0009],于温度20~22 ℃,湿度60%~65%的环境下饲养,光照10~12 h/d。
MRBP无创血压仪 美国IITC公司;SP-Max3500FL酶标仪 美国Bio Tek Instruments,Inc公司;S-42叠加式恒温振荡器 苏州捷美电子有限公司;R202-2旋转蒸发器 常州诺基仪器有限公司;SHZ-DⅢ循环真空泵 郑州市仪特仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 水煎剂的制备
人参组水煎剂制备:去除人参根部,将其粉碎,称取粉碎的人参600 g,按1:10比例加入蒸馏水混合搅拌均匀浸泡一夜。将人参浸泡液在95 ℃下浸提2 h后冷却、过滤,然后进行二次浸提、过滤,将两次提取液混合后,因每人每天摄入人参剂量为3 g/60 kg,因此不同倍数的大鼠灌胃剂量为2、4 g/kg。用旋转蒸发器在70 ℃下浓缩成浓度为133、267 g/L人参提取液,浓缩完毕后,冷冻备用;配伍组水煎剂制备:按1:4比例称取粉碎人参与蒲公英根,加10倍蒸馏水浸泡一夜,将人参浸泡液在95 ℃下浸提两次,用旋转蒸发器在70 ℃下浓缩成提取液。浓缩完毕后,冷冻备用。
1.2.2 动物分组
40只SD大鼠适应性饲养7 d后,按体质量随机分为正常组、2 g/kg人参提取液组、4 g/kg人参提取液组、2 g/kg配伍组、4 g/kg配伍组,每组各8只。各组每天同一时间段进行灌胃,正常对照组每日每次予以蒸馏水,1 次/1 d,连续灌胃19 d。实验饲料为延边大学饲料库加工,饲料配比为:玉米面(40%)、白面(15.4%)、豆粕(20%)、芝麻饼(5%)、麦麸(5%)、鱼粉(6%)、酵母粉(2%)、骨粉(2%)、豆油(1%)、盐(1%)、鸡蛋(2%)、多维(0.4%)、生长素(0.2%),且实验过程均按照正常饲养动物规定进行,且符合延边大学动物福利伦理要求。
1.2.3 指标检测
在实验过程中观察大鼠体毛变化及活动状态。每2 d称量各组大鼠体质量;每5 d对各组大鼠的剩余摄食量和饮水量进行称量并统计计算;每3 d测量各组大鼠体温(肛温)。
每6 d测量各组大鼠血压,连接好机器后,将大鼠放入支架,移开端板,使其爬进丙烯酸管的尾部侧开口,待大鼠进入固定器,安装末端板。然后将大鼠尾巴穿过尾袖传感器,使尾根部在其传感器处,将限制器放在系统的加热部分盖上盖子,让大鼠适应3~5 min,并确保腔室温度达到34 ℃时启动实时运行,在触摸屏上查看脉冲泳道显示,观察是否有脉冲检测显示,并进行记录[16−17]。
灌胃第19 d,所有实验大鼠禁食后取血。血液样本在室温下保持30 min后,以3000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液后用ELISA法检测神经系统、内分泌系统、免疫系统的生化指标。
1.2.4 血清中5-HT、TSH、17-OHCS、CORT测定
将各试剂移至室温0.5 h,量取浓缩洗涤液稀释混匀备用;设置标准品孔、空白孔和样本孔,加入不同浓度的溶液,混匀,贴上封板膜,置37 ℃温育60 min;丢弃液体,将洗涤液填满每个孔,静置1 min后扔掉洗涤液;每孔加入酶标亲和素50 μL(空白对照孔除外),混匀,贴上封板膜,置37 ℃温育30 min;每孔加入底物A和B,37 ℃避光刺激15 min;以450 nm波长测定各孔的OD值。
1.2.5 血清中NE、IL-2、IL-6、TNF-α测定
在室温下平衡60 min后,从铝箔袋中取出所需板条,用子密封袋密封剩余板条,并将其放回4 ℃;设置标准品孔、空白孔和样本孔,加入不同浓度的溶液,混匀,贴上封板膜,置37 ℃温育60 min;清除液体,每孔加满洗涤液,放置1 min,丢弃液体,重复洗板5次。每孔加入底物A和B各50 μL,37 ℃避光刺激15 min;每孔加入终止液50 μL,15 min内,以450 nm波长处测定各孔的OD值。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2019和SPSS 19.0对实验结果进行统计分析和处理,以(±s)表示所得数据,P<0.05则表示组间有显著性差异,P<0.01则表示组间差异极显著,由Excel 2019及GraphPad Prism 8.0进行绘制图表。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 人参与蒲公英根配伍调节体内“上火”作用
2.1.1 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体征的影响
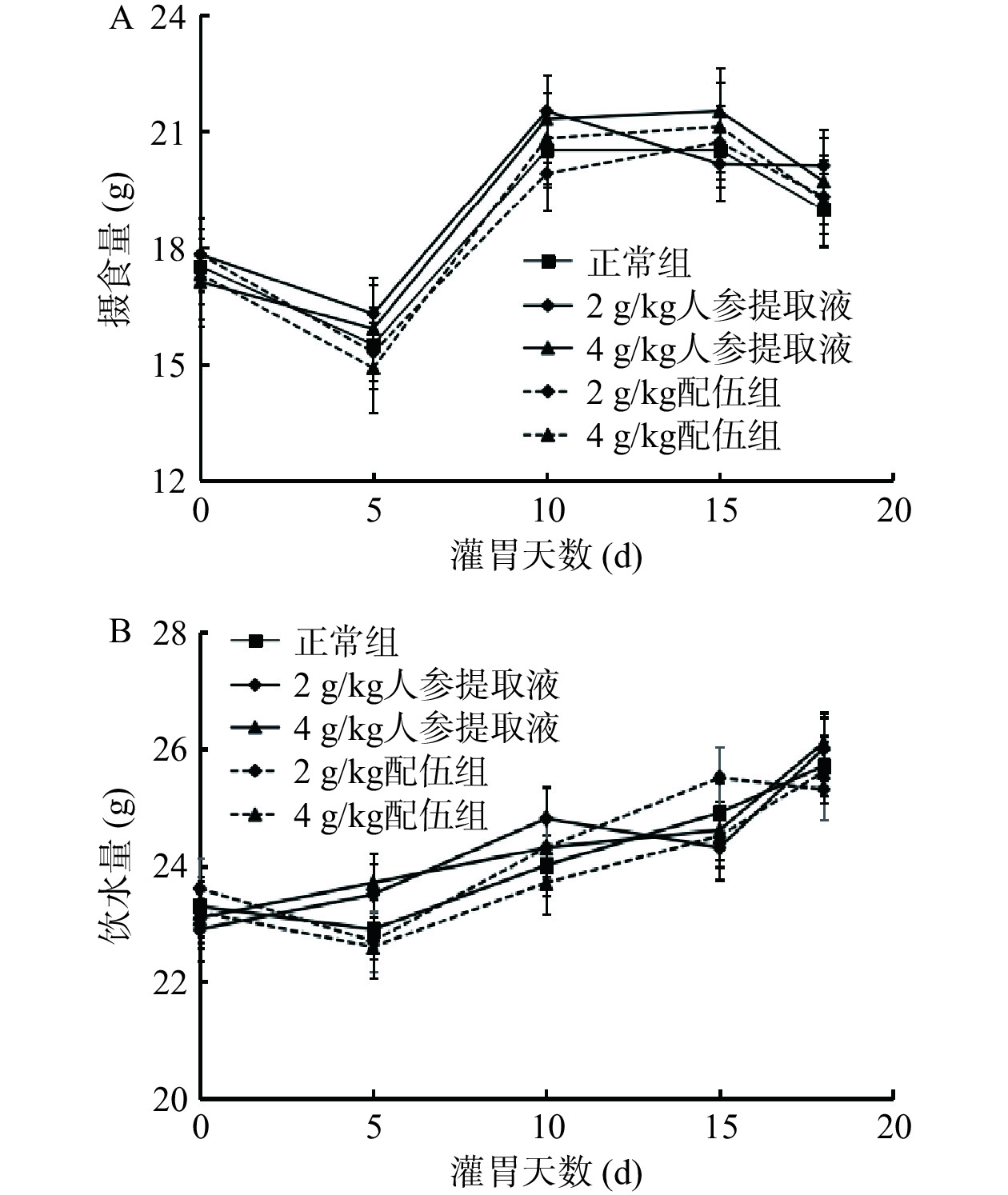
由图1可知各组大鼠摄食量、饮水量的变化情况,灌胃19 d,各组大鼠的摄食量、饮水量差异均无统计学意义,说明服用人参与蒲公英根对大鼠摄食量及饮水量无副作用。各组大鼠体质量均呈稳定增长趋势,实验结果表明,服用人参及蒲公英根不会对体质量产生较大影响(表1)。第18 d,与正常组比较,各“上火”人参组大鼠活动均明显增加,捉拿时四肢挣扎剧烈,不易抓取,且出现不同程度毛发蓬松的现象,符合“上火”动物模型的体征表象[18−19],其中4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠毛发蓬松,烦躁多动的现象更明显。
表 1 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体质量的影响(n=8,g)Table 1. Effect of ginsing in the compatibility of dandelion root on the body mass of "Shanghuo" model rats (n=8, g)组别 0 d 18 d 正常组 209.38±15.45a 360.00±18.32a 2 g/kg人参提取液组 207.50±12.25a 345.71±13.36a 4 g/kg人参提取液组 208.13±11.32a 338.13±23.90a 2 g/kg配伍组 204.38±18.41a 342.14±26.28a 4 g/kg配伍组 204.38±17.20a 348.00±45.61a 注:同一列中不同字母表示各组大鼠纵向比较具有显著差异(P<0.05)。 2.1.2 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体温的影响
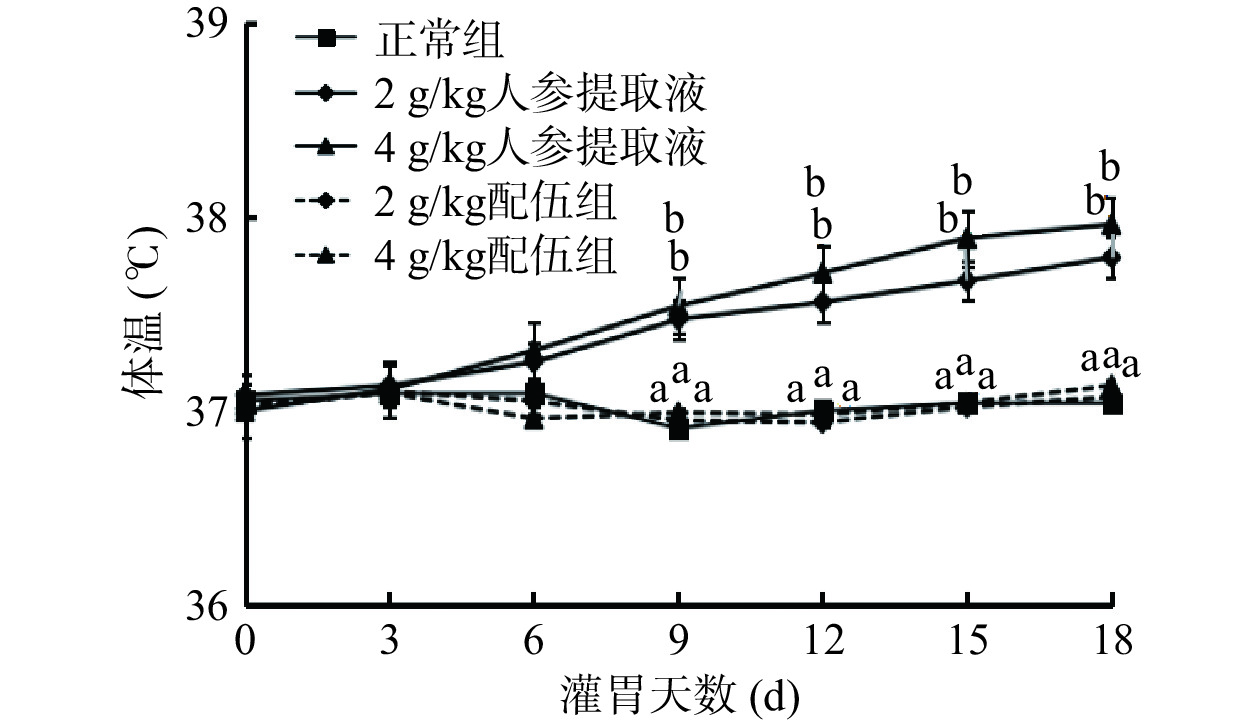
人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体温的影响如图2所示。与正常组比较,2 g/kg人参提取液组与4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠体温均随灌胃时间的延长而缓慢增长。与人参各组相比较,2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组体温下降,且存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。2、4 g/kg配伍组与正常组大鼠体温变化基本一致,说明2、4 g/kg配伍组均可有效调节“上火”所引起的体温升高现象。
![]() 图 2 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体温的影响注:不同字母表示各组大鼠比较具有显著差异(P<0.05),图3同。Figure 2. Effect of ginsing in dandelion root compatibility on body temperature of rats with "Shanghuo" model
图 2 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体温的影响注:不同字母表示各组大鼠比较具有显著差异(P<0.05),图3同。Figure 2. Effect of ginsing in dandelion root compatibility on body temperature of rats with "Shanghuo" model2.1.3 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠血压的影响
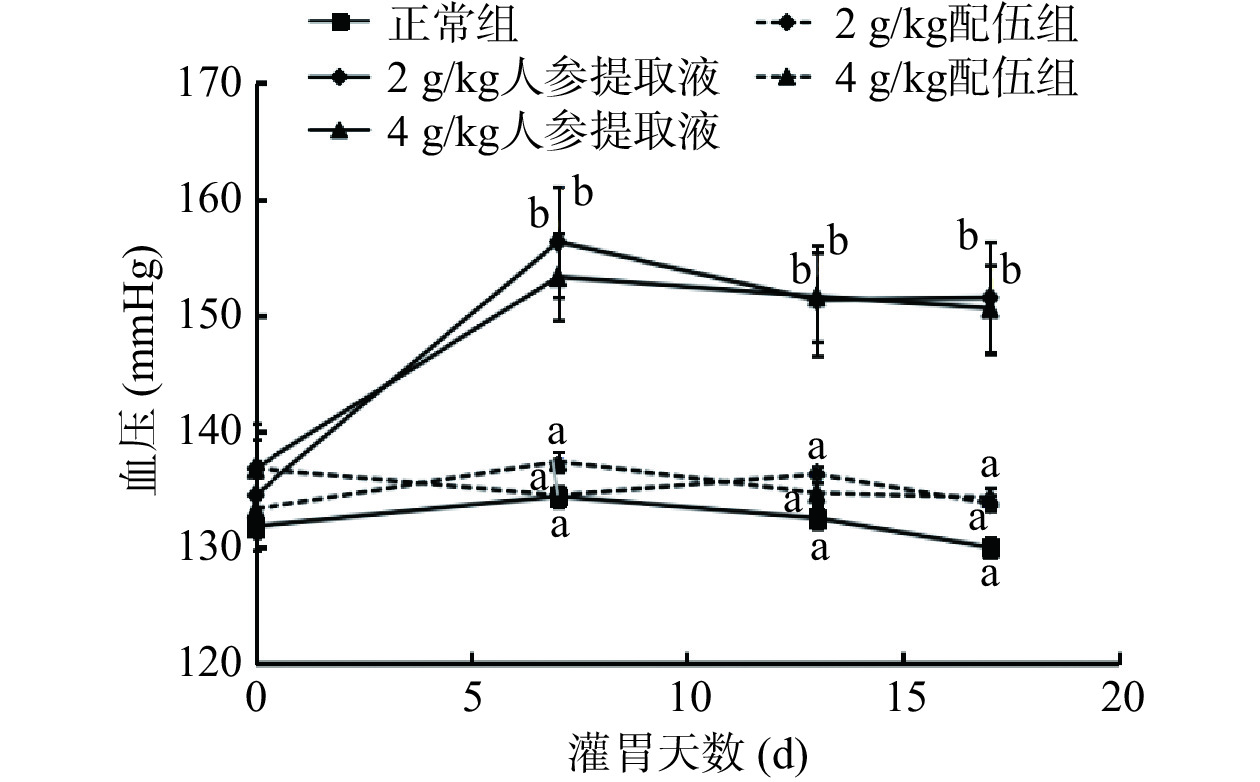
人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠血压的影响由图3所示。由图3可知,与正常组比较,2 、4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠血压均升高且呈高血压状态,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);与人参各组比较,2、4 g/kg配伍组大鼠血压降低,且与正常组一致,都在正常收缩压范围内(大鼠正常血压水平范围:90~140 mmHg[20−21]),收缩压差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) 。
2.1.4 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠神经系统的影响
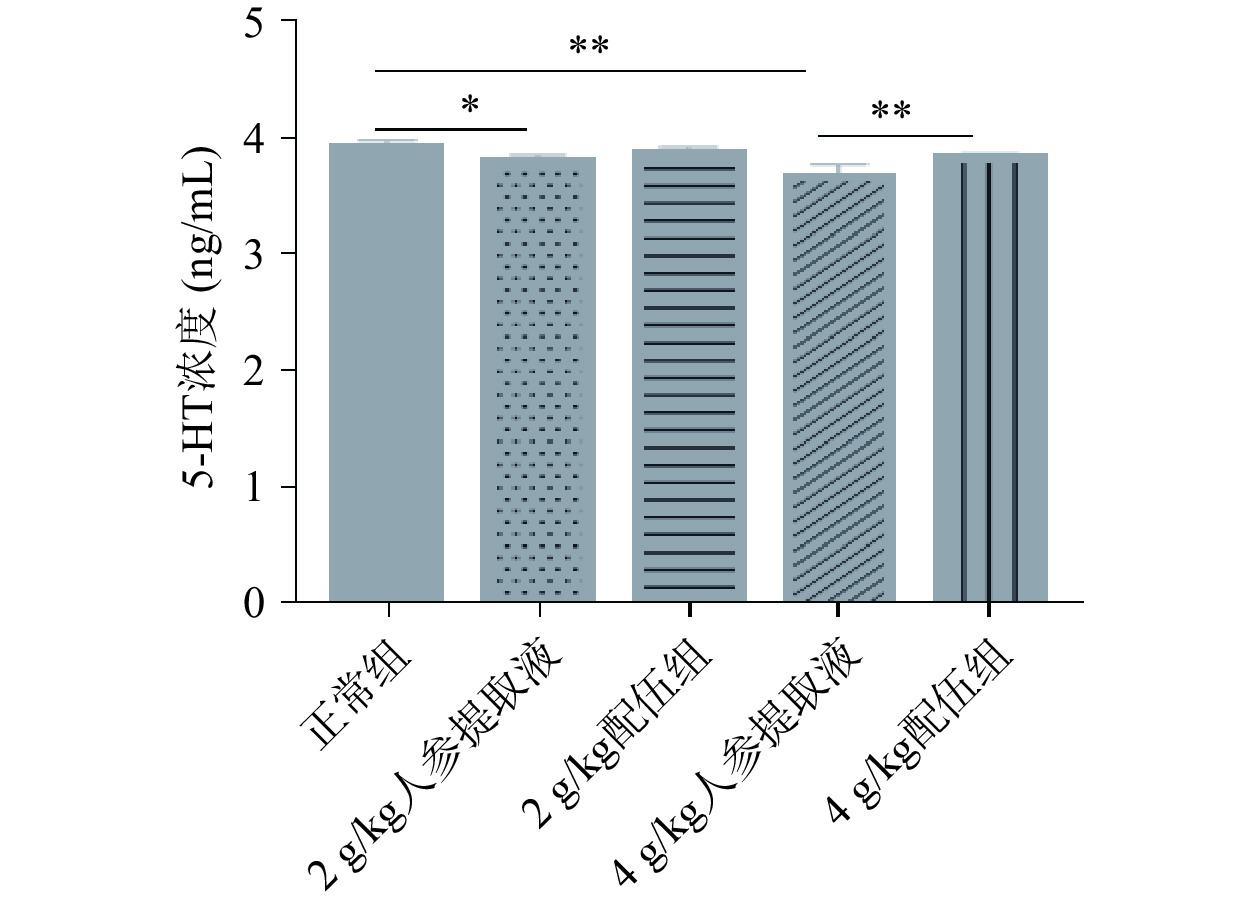
5-HT作为一种单胺类神经递质,又是一种血管活性物质,在脑内分布极为广泛,在中枢神经系统和周围组织中发挥着多种生理作用[22]。当脑内5-HT含量降低时,会出现一系列抑郁症、情绪不安、睡眠障碍、认知障碍、强迫行为和攻击行为等[23]。由图4可知,各组大鼠5-HT含量变化,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组“上火”大鼠5-HT含量均降低,具有显著性差异(P<0.05),因此会出现各人参组大鼠活动增加且抓取时挣扎剧烈的现象。与4 g/kg人参提取液组比较,4 g/kg配伍组5-HT含量回升且有极显著差异(P<0.01),可有效调节5-HT含量趋于恢复正常组的正常水平。因此本实验说明人参组可使5-HT含量下降;4 g/kg配伍组可以调节机体5-HT含量,缓解“上火”引起的情绪焦虑、抑郁等情况。
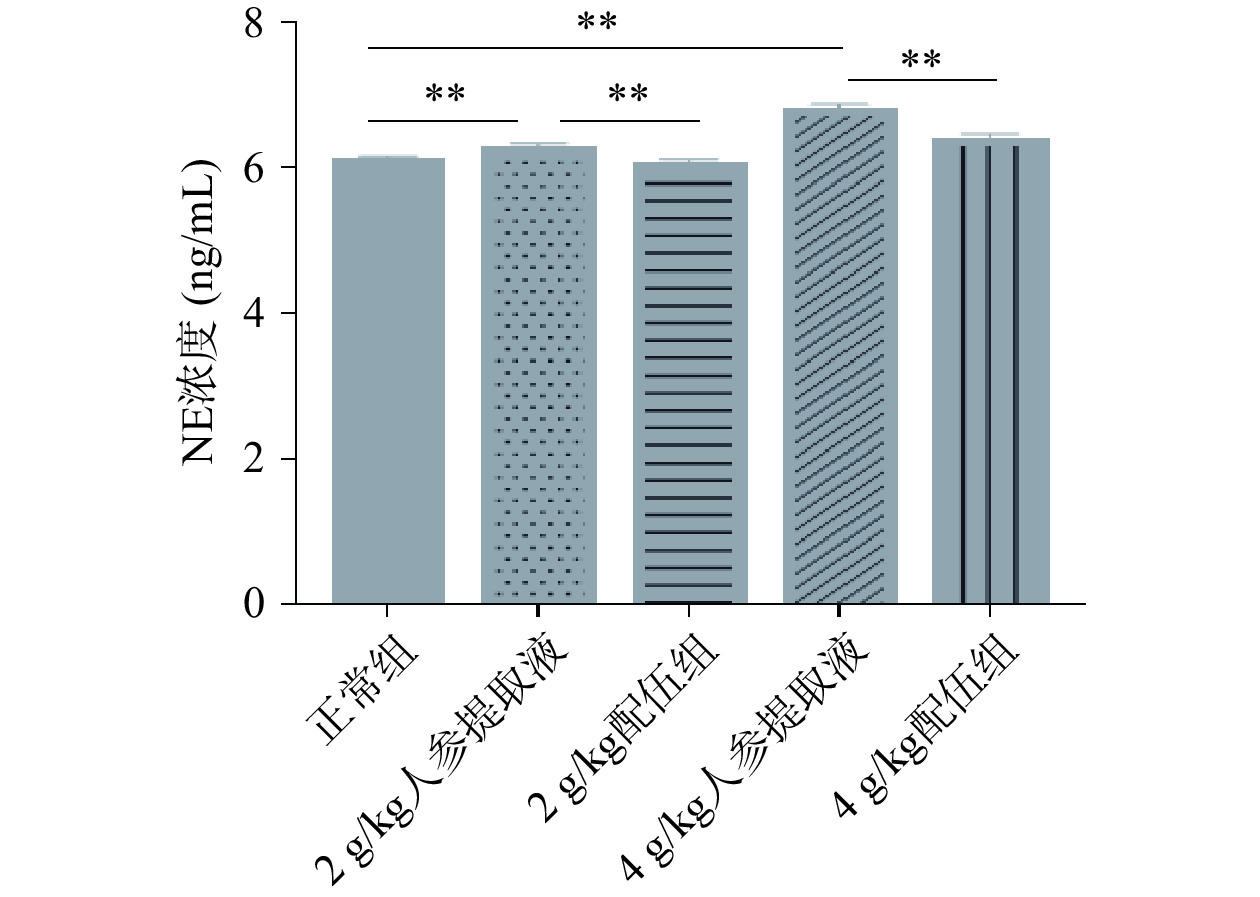
NE是中性粒细胞合成、储存和释放的最重要的蛋白酶之一。它具有极强的破坏性,能够破坏组织,并且分解几乎所有的细胞外基质蛋白和许多重要的血浆蛋白[24−25]。由图5可知各组大鼠NE含量变化,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组NE含量均显著升高,有显著性差异(P<0.01);与人参各组比较,2 、4 g/kg配伍组NE含量均降低且有显著性差异(P<0.01),其中4 g/kg配伍组大鼠NE含量显著降低(P<0.01)且含量高于正常组。含量比较为,4 g/kg配伍组>正常组>2 g/kg配伍组。因此4 g/kg配伍组可有效缓解抑郁情绪,可在正常组的水平上增加NE含量以预防抑郁情绪的产生。
2.1.5 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠内分泌系统的影响
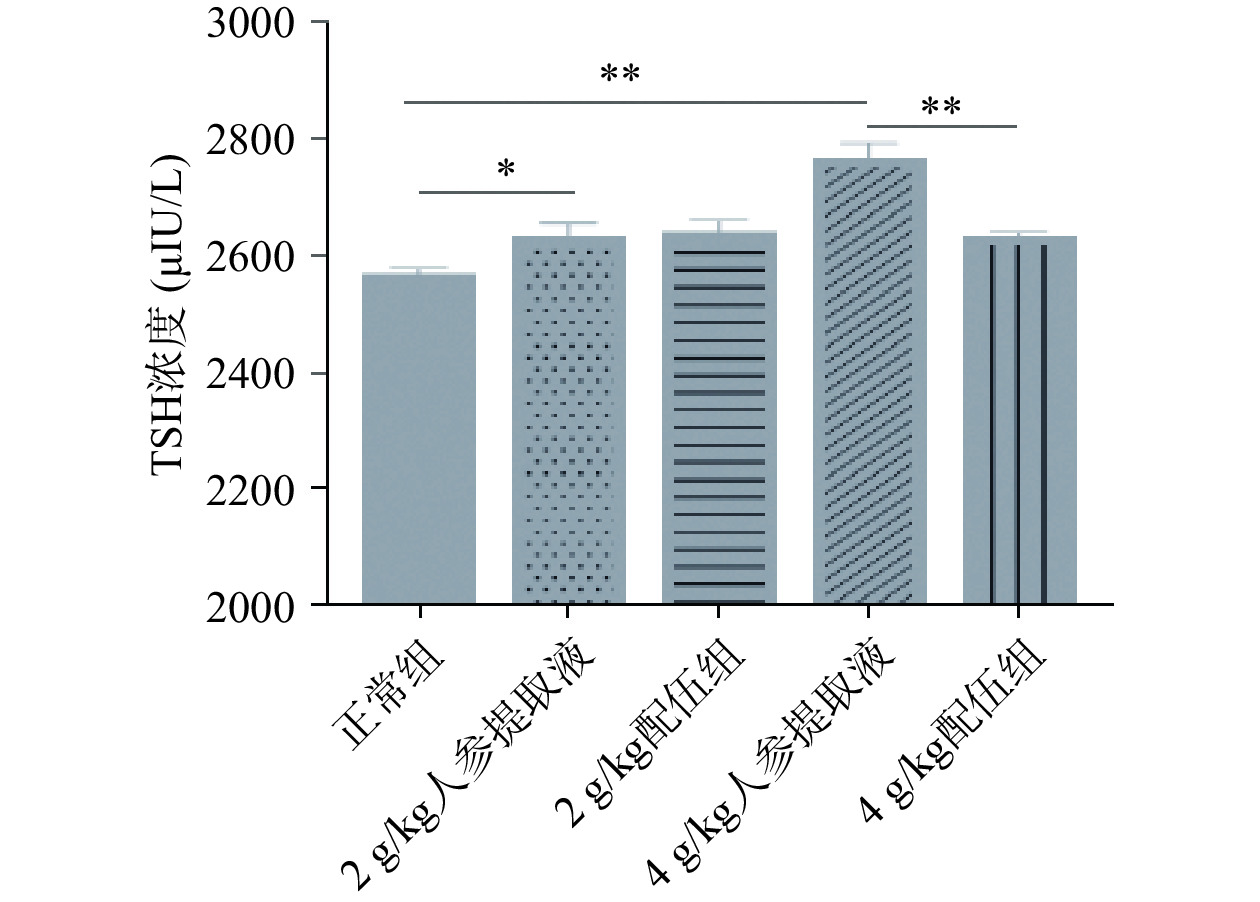
TSH是由腺垂体分泌的一种糖蛋白,是直接调节甲状腺功能的关键激素,是反映下丘脑-垂体-甲状腺轴功能的敏感指标[26−28]。由图6可知,各组大鼠TSH含量变化,实验结果显示,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠TSH含量均显著升高且具有显著性差异(P<0.05);与人参各组比较,2 g/kg配伍组大鼠TSH含量差异无统计学意义,而4 g/kg配伍组TSH含量明显下降且具有显著性差异(P<0.01),4 g/kg配伍组TSH含量略高于正常组。
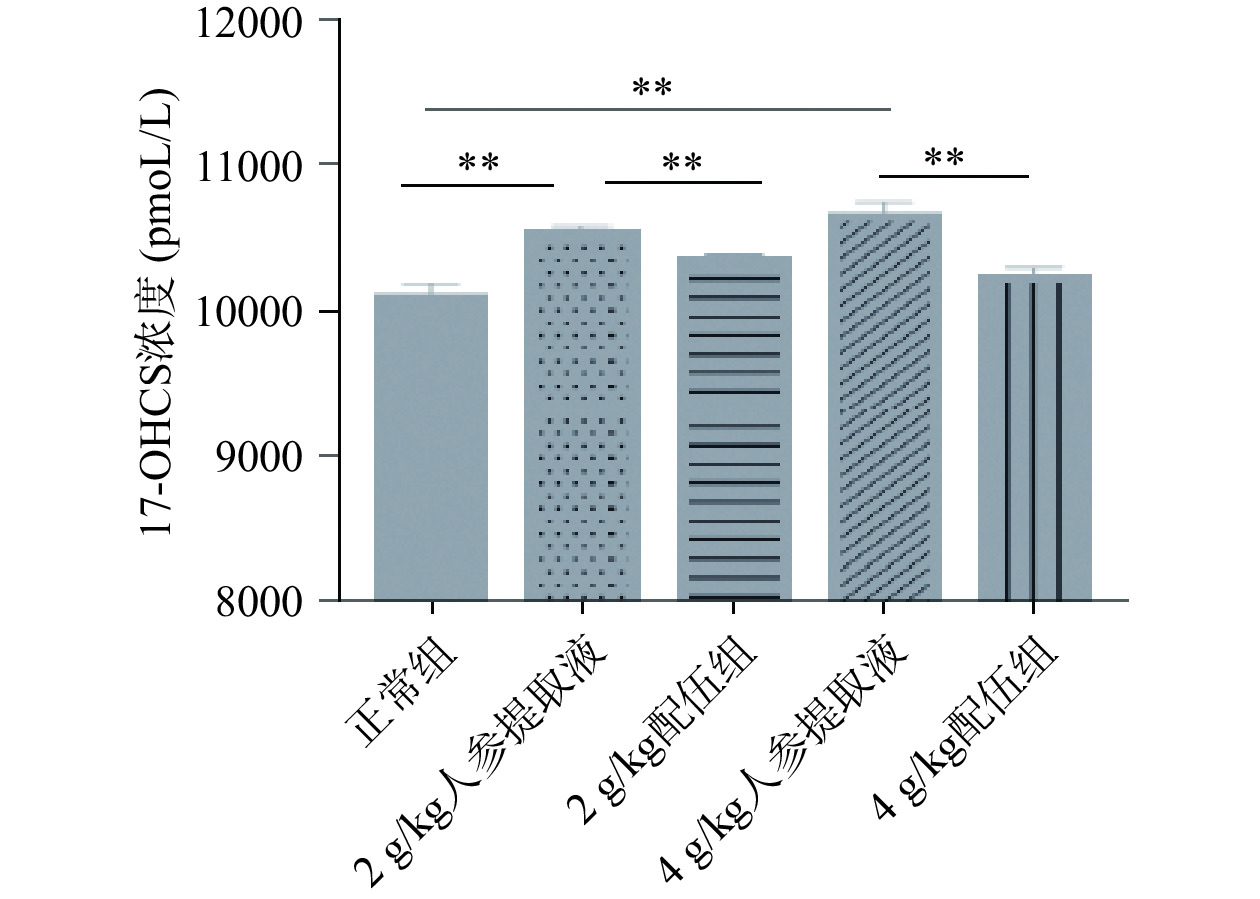
17-OHCS是指肾上腺皮质分泌的皮质醇、皮质素和它们的代谢产物,可反映交感神经-肾上腺皮质功能[29−30]。当肾上腺皮质功能亢进时,外周17-OHCS的排出量增加。由图7可知各组大鼠17-OHCS含量变化,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠17-OHCS含量均显著升高(P<0.01);与人参各组比较,2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组大鼠17-OHCS含量均下降具有极显著性差异(P<0.01),其中2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组17-OHCS含量水平略高于正常组。与正常组比较,本实验检测的各“上火”人参组血清TSH和17-OHCS的含量都显著上升。因此本实验结果表明,在确认人参温热特性的同时,人参“上火”模型存在交感神经-肾上腺功能的增强,而2、4 g/kg配伍组配伍可较好的保留服用人参的温热效果,还可缓解因“上火”引起的TSH、17-OHCS含量升高的症状。
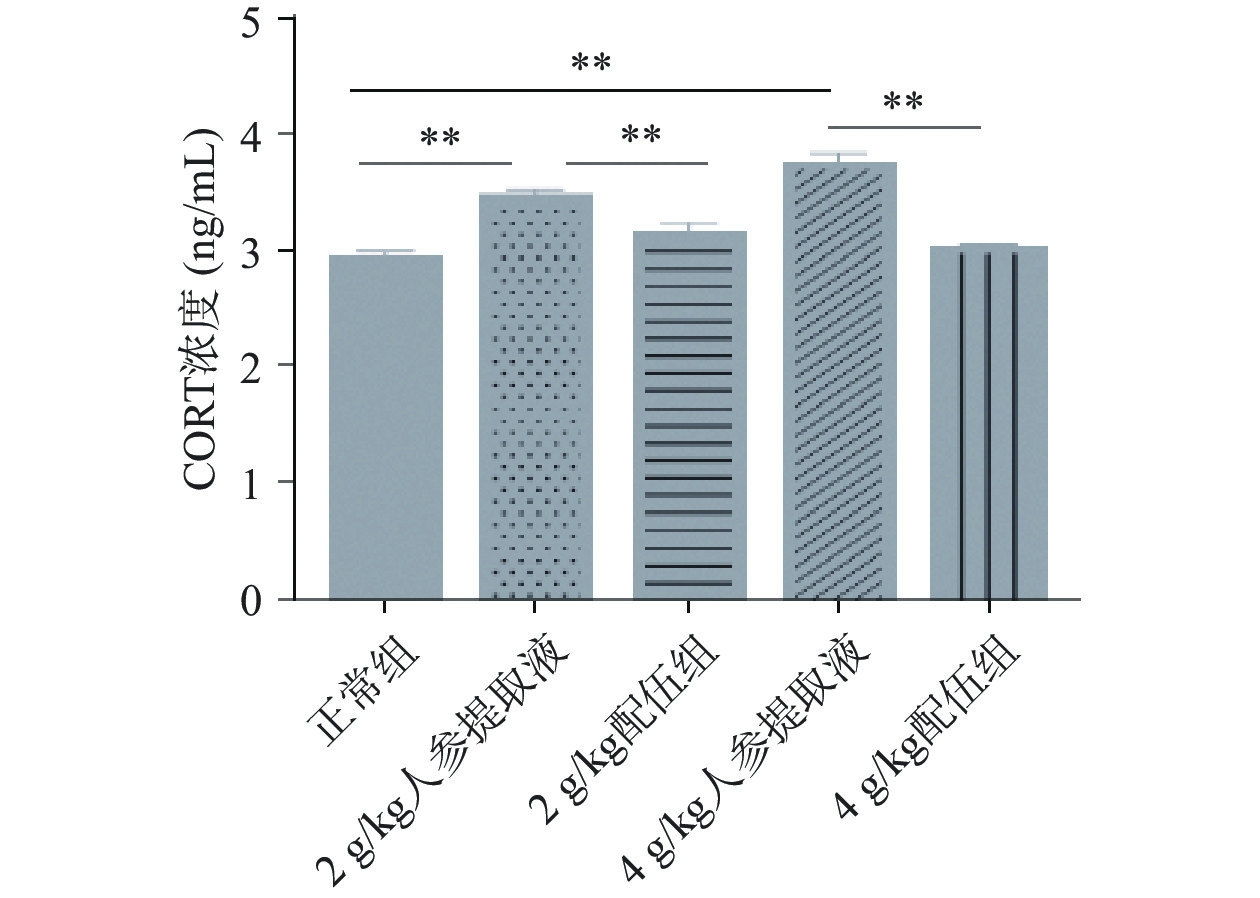
CORT是肾上腺皮质分泌的一种糖皮质激素,其分泌受下丘脑促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素和垂体促肾上腺皮质激素的调控[31−32]。由图8可知,各组大鼠CORT含量变化,结果显示,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠血清中CORT含量均明显升高且具有显著性差异(P<0.01);与人参各组比较,2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组大鼠血清中CORT含量均极显著性降低(P<0.01),且2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组CORT含量均略高于正常组。因此,2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组可较好调节因服用人参引起的机体CORT含量升高的症状。
2.1.6 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠免疫系统的影响
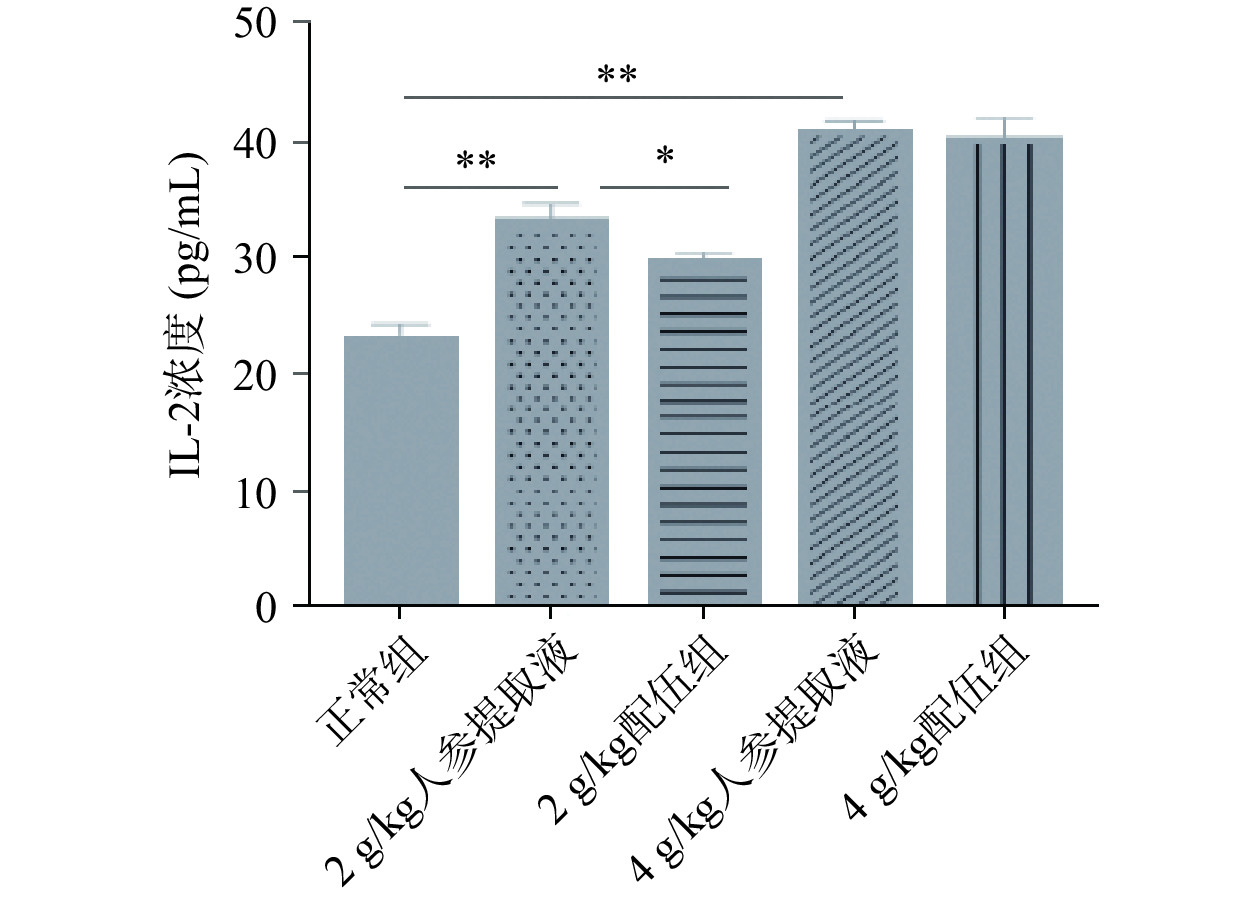
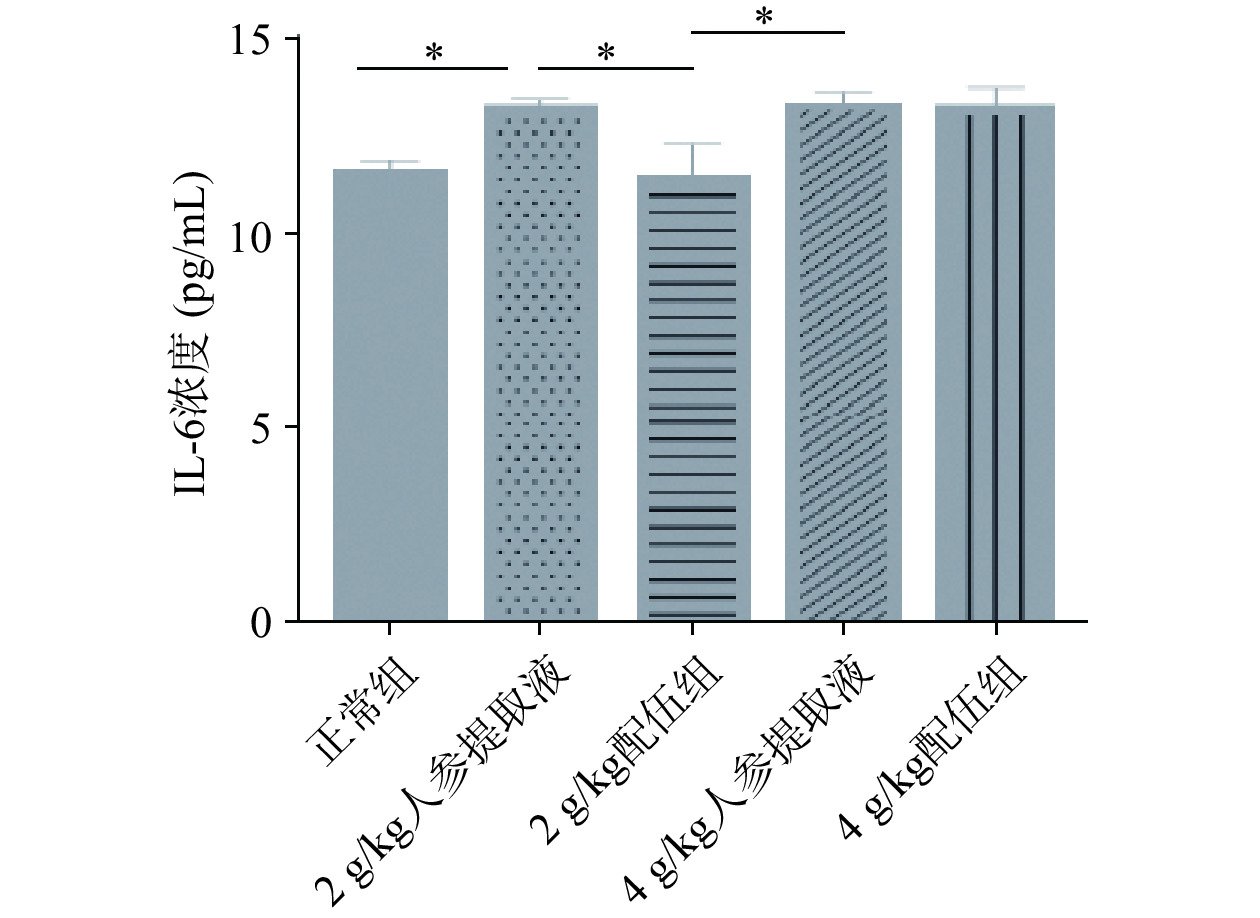
白细胞介素(Interleucine,IL)是指在白细胞或免疫细胞之间相互作用、相互协调以完成造血和免疫调节功能的淋巴因子。IL在传递信息的同时,激活和调节免疫细胞,介导T细胞和B细胞的活化、增殖与分化,在炎症反应中发挥重要作用[33−36]。由图9~图10可知,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠IL-2、IL-6含量均升高,且具有显著性差异;与人参各组比较,4 g/kg配伍组大鼠IL-2、IL-6含量变化差异无统计学意义,而2 g/kg配伍组IL-2、IL-6含量下降且差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。IL-2含量比较为,4 g/kg配伍组>2 g/kg配伍组>正常组,IL-6含量比较为,4 g/kg配伍组>正常组>2 g/kg配伍组。综合分析,2 g/kg配伍组与4 g/kg配伍组比较,4 g/kg配伍组可较好的保留因服用人参提高机体免疫的效果。因此说明4 g/kg配伍组可调节因服用人参引起的“上火”症状,同时还可较好的增强大鼠机体的免疫功能。
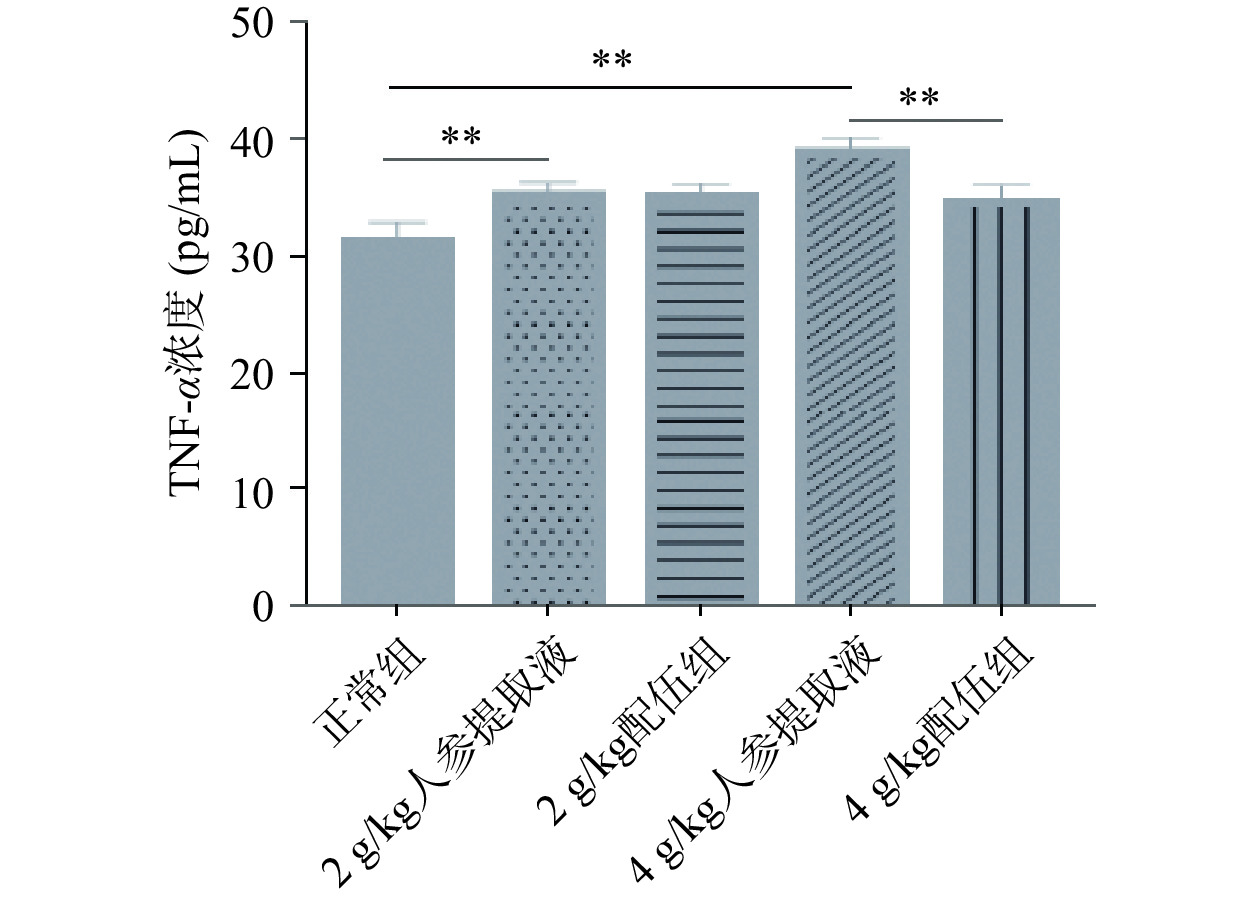
TNF-α是由单核-巨噬细胞产生的多显性细胞因子,具有调节免疫应答,促进细胞生长分化等多种生理功能,其生物学活性是通过细胞表面的特异性受体传递信号的,是具有生物学活性的重要炎性介质之一[37−38]。由图11可知,各组大鼠TNF-α含量变化,与正常组比较,2、4 g/kg人参提取液组大鼠TNF-α含量均升高且具有显著性差异(P<0.01);与人参各组比较,2 g/kg配伍组大鼠TNF-α含量无明显变化,4 g/kg配伍组大鼠TNF-α含量降低且具有显著性差异(P<0.01),且其含量高于正常组,因此本实验结果证明人参能使TNF-α含量增加,并刺激淋巴细胞增殖,而4 g/kg配伍组可有效改善TNF-α含量的增加,从而抑制炎症反应。
3. 结论
本实验针对中医养生配伍理论与食品相结合,把人参与蒲公英根进行配伍,结果表明,配伍后可改善动物体温及血压,同时改善神经系统(5-HT升高,NE降低)、内分泌系统(TSH、17-OHCS、CORT降低)、免疫系统(IL-2、IL-6、TNF-α降低)相关指标的分泌。
因此,在人参与蒲公英跟配伍缓解“上火”模型组大鼠的相关生化指标的基础上,后续可通过利用代谢组学等技术将配伍进行深层次研究,体现配伍机制的差异以及不同配伍比例化学成分的变化规律,明确调节“上火”症状的协同作用,提高其应用范围,以期更全面地发挥人参与蒲公英根配伍的优势作用,为复方配伍规律及食品开发提供新方法。
-
图 2 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体温的影响
注:不同字母表示各组大鼠比较具有显著差异(P<0.05),图3同。
Figure 2. Effect of ginsing in dandelion root compatibility on body temperature of rats with "Shanghuo" model
表 1 人参与蒲公英根配伍对“上火”模型大鼠体质量的影响(n=8,g)
Table 1 Effect of ginsing in the compatibility of dandelion root on the body mass of "Shanghuo" model rats (n=8, g)
组别 0 d 18 d 正常组 209.38±15.45a 360.00±18.32a 2 g/kg人参提取液组 207.50±12.25a 345.71±13.36a 4 g/kg人参提取液组 208.13±11.32a 338.13±23.90a 2 g/kg配伍组 204.38±18.41a 342.14±26.28a 4 g/kg配伍组 204.38±17.20a 348.00±45.61a 注:同一列中不同字母表示各组大鼠纵向比较具有显著差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 申时利. 人参栽培技术研究[J]. 中国农业文摘-农业工程,2016,28(4):41−43. [SHEN S L. Research on ginseng cultivation techniques[J]. China Agricultural Digest-Agricultural Engineering,2016,28(4):41−43.] SHEN S L. Research on ginseng cultivation techniques[J]. China Agricultural Digest-Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 28(4): 41−43.
[2] 刘伟, 刘永博, 王梓, 等. 人参的化学成分与转化机理研究进展[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2023,45(6):664−673. [LIU W, LIU Y B, WANG Z, et al. Research progress on the chemical composition and transformation mechanism of ginseng[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,2023,45(6):664−673.] LIU W, LIU Y B, WANG Z, et al. Research progress on the chemical composition and transformation mechanism of ginseng[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2023, 45(6): 664−673.
[3] 于京华, 岳喜典. 人参的保健功能及其在食品中的应用[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(21):218−224. [YU J H, YUE X D. The health function of ginseng and its application in Food[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(21):218−224.] YU J H, YUE X D. The health function of ginseng and its application in Food[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(21): 218−224.
[4] 陈俞宇, 隋华, 张莉, 等. 服用人参导致“上火”的研究综述[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2018,20(4):597−602. [CHEN Y Y, SUI H, ZHANG L, et al. Review of ginseng ginseng to "ShangHuo"[J]. World Science and Technology-Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,20(4):597−602.] CHEN Y Y, SUI H, ZHANG L, et al. Review of ginseng ginseng to "ShangHuo"[J]. World Science and Technology-Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 20(4): 597−602.
[5] 蔡鸿彦, 张彦峰, 武晓璐, 等. 不同年龄人群食用人参 “上火”临床研究[J]. 吉林中医药,2017,37(11):1131−1133. [CAI H Y, ZHANG Y F, WU X L, et al. Clinical study on ginseng consumption by people of different ages[J]. Jilin Traditional Chinese Medicine,2017,37(11):1131−1133.] CAI H Y, ZHANG Y F, WU X L, et al. Clinical study on ginseng consumption by people of different ages[J]. Jilin Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(11): 1131−1133.
[6] 王超杰, 刘甜甜, 曹明明, 等. 基于古方数据挖掘珍稀中药人参的用药特点与配伍规律[J]. 世界中医药,2022,17(14):2066−2070,2074. [WANG C J, LIU T T, CAO M M, et al. Mining the drug characteristics and compatibility rules of rare Chinese medicine ginseng based on ancient prescription data[J]. The World of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,17(14):2066−2070,2074.] WANG C J, LIU T T, CAO M M, et al. Mining the drug characteristics and compatibility rules of rare Chinese medicine ginseng based on ancient prescription data[J]. The World of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 17(14): 2066−2070,2074.
[7] XIE Y, MAI C T, ZHENG D C, et al. Wutou decoction ameliorates experimental rheumatoid arthritis via regulatin g NF-κB and Nrf2:Integrating efficacy-oriented compatibility of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Phytomedicine,2021,85(10):153522.
[8] 王新策, 孙斐, 傅茂润, 等. 蒲公英功能活性及在食品中的应用研究[J]. 中国果菜,2021,41(2):28−33. [WANG X C, SUN F, FU M R, et al. Dandelion functional activity and its application in food products[J]. Chinese Fruit Vegetables,2021,41(2):28−33.] WANG X C, SUN F, FU M R, et al. Dandelion functional activity and its application in food products[J]. Chinese Fruit Vegetables, 2021, 41(2): 28−33.
[9] KIM J H, BAIK S H. Preparation and characterization of fermented dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) beverage using Lactobacillus acidophilus F46 having cinnamoyl esterase activity[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2015,24(2):583−593. doi: 10.1007/s10068-015-0076-1
[10] JEDREJEK D, LIS B, ROLNIK A, et al. Comparative phytochemical, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and haemostatic studies of Taraxacum officinale root preparations[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2019,126(1):233−247.
[11] 赵婷, 谢冠群, 徐莉, 等. 从AMPK能量调节功能探讨红参上火机制[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2018,42(10):797−803,809. [ZHAO T, XIE G Q, XU L, et al. Explore the mechanism of red ginseng and heat increase from the energy regulation function of AMPK[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine University,2018,42(10):797−803,809.] ZHAO T, XIE G Q, XU L, et al. Explore the mechanism of red ginseng and heat increase from the energy regulation function of AMPK[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine University, 2018, 42(10): 797−803,809.
[12] XU X, DOU D Q. The ginseng's fireness is associated with the lowering activity of liver Na+-K+-ATPase[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2016,190:241−250. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.024
[13] FARIA T C, NASCIMENTO C, DE VASCONCELOS S D D, et al. Literature review on the biological effects of Taraxacum officinale plant in therapy[J]. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutica l Research and Development,2019,7(3):94−99. doi: 10.22270/ajprd.v7i3.502
[14] FENTON-NAVARRO B, MONTES F O, HERNANDEZ A V. Active compounds of medicinal plants, mechanism for antioxidant and beneficial effects[J]. Phyton, International Journal of Experimental Botany,2019,88(1):1−10.
[15] 卢训丛, 胡卫. 蒲公英临床配伍新探[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2011,17(11):1277−1278. [LU X C, HU W. New exploration on clinical compatibility of Taraxacum[J]. China Journal of Basic Medicine in Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011,17(11):1277−1278.] LU X C, HU W. New exploration on clinical compatibility of Taraxacum[J]. China Journal of Basic Medicine in Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 17(11): 1277−1278.
[16] 焦海霞, 李凌, 余涓, 等. 尾套法和颈动脉法测定急性应激大鼠血压变化值的比较[J]. 福建医科大学学报,2006(4):404−405. [JIAO H X, LI L, YU J, et al. Comparison of BP change values in acute stressed rats by tail cuff and carotid method[J]. The Journal of Fujian Medical University,2006(4):404−405.] JIAO H X, LI L, YU J, et al. Comparison of BP change values in acute stressed rats by tail cuff and carotid method[J]. The Journal of Fujian Medical University, 2006(4): 404−405.
[17] 李培慈, 徐斌, 孔古娅, 等. 新一代动物无创血压测定仪的研制及性能检验[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2006(1):122−124. [LI P C, XU B, KONG G Y, et al. Development and performance test of a new generation of animal non-invasive blood pressure tester[J]. The Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology,2006(1):122−124.] LI P C, XU B, KONG G Y, et al. Development and performance test of a new generation of animal non-invasive blood pressure tester[J]. The Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology, 2006(1): 122−124.
[18] 陈仙英, 徐莉, 李思敏, 等. 红参、黄芪诱导的大鼠实热证模型血液内环境改变及分析[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2018,42(10):790−796. [CHEN X Y, XU L, LI S M, et al. Analysis of blood environment changes in rat real heat model induced by red ginseng and Astragalus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine University,2018,42(10):790−796.] CHEN X Y, XU L, LI S M, et al. Analysis of blood environment changes in rat real heat model induced by red ginseng and Astragalus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine University, 2018, 42(10): 790−796.
[19] 张喜召, 包洁, 窦晓兵, 等. 基于AMPK-PGC-1α信号通路探讨“上火”动物模型的发病机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(4):2002−2006. [ZHANG X Z, BAO J, DOU X B, et al. Exploring the pathogenesis of the "Shanghuo" animal model based on the AMPK-PGC-1α signaling pathway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,35(4):2002−2006.] ZHANG X Z, BAO J, DOU X B, et al. Exploring the pathogenesis of the "Shanghuo" animal model based on the AMPK-PGC-1α signaling pathway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 35(4): 2002−2006.
[20] 杨丽丽, 李文林, 曾莉, 等. 基于证据综合加权方法评价人参干预血糖、血压及血脂文献筛选研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2019,37(3):555−558. [YANG L L, LI W L, ZENG L, et al. Literature screening study of ginseng intervention in blood glucose, blood pressure and blood lipid based on comprehensive evidence weighting method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,37(3):555−558.] YANG L L, LI W L, ZENG L, et al. Literature screening study of ginseng intervention in blood glucose, blood pressure and blood lipid based on comprehensive evidence weighting method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 37(3): 555−558.
[21] 江一川, 丁春予, 田原, 等. 人参超微粉及水提物对自发性高血压大鼠血压的影响[J]. 人参研究,2017,29(2):2−5. [JIANG Y C, DING C Y, TIAN Y, et al. Effect of ginseng ultrapowder and aqueous extract on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. Ginseng Research,2017,29(2):2−5.] JIANG Y C, DING C Y, TIAN Y, et al. Effect of ginseng ultrapowder and aqueous extract on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. Ginseng Research, 2017, 29(2): 2−5.
[22] 刘铭. 齐拉西酮联合奥氮平治疗精神分裂症患者临床效果及对血清BDNF、5-HT、NE水平的影响[J]. 中国医学创新,2021,18(32):152−155. [LIU M. Clinical effect of ziprazidone plus olanazapine and effects on serum BDNF, 5-HT and NE levels in schizophrenia patients[J]. The Chinese Medical Innovation,2021,18(32):152−155.] LIU M. Clinical effect of ziprazidone plus olanazapine and effects on serum BDNF, 5-HT and NE levels in schizophrenia patients[J]. The Chinese Medical Innovation, 2021, 18(32): 152−155.
[23] FLANIGAN M E, HON O J, D'AMBROSIO S, et al. Subcortical serotonin 5HT2c receptor-containing neurons sex-specifically regulate binge-like alcohol consumption, social, and arousal behaviors in mice[J]. Nature Communications,2023,14(1):1800. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36808-2
[24] DEL P J, MOYANO P, RUIZ M, et al. Amitraz changes NE, DA and 5-HT biosynthesis and metabolism mediated by alterations in estradiol content in CNS of male rats[J]. Chemosphere,2017,181(1):518−529.
[25] 刘靖, 涂绍忠, 陈湘君, 等. NE刺激对HaCaT细胞分泌NE、Trappin-2的影响及银屑1号的干预[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2019,46(8):1740−1742. [LIU J, XU S Z, CHEN X J, et al. Effect of NE stimulation on NE and Trappin-2 secretion by HaCaT cells and the intervention of psoriasis number 1[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,46(8):1740−1742.] LIU J, XU S Z, CHEN X J, et al. Effect of NE stimulation on NE and Trappin-2 secretion by HaCaT cells and the intervention of psoriasis number 1[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 46(8): 1740−1742.
[26] MA R S, MORSHED S, LATIF R, et al. The influence of thyroid-stimulating hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibodies on osteoclastogenesis[J]. Thyroid: Official Journal of the American Thyroid Association,2011,21(8):897−906. doi: 10.1089/thy.2010.0457
[27] CHEN J, SHI M M, WANG N, et al. TSH inhibits eNOS expression in HMEC-1 cells through the TSHR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Annales d'Endocrinologie,2019,80(5-6):273−279. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2019.06.007
[28] 胡春枝, 左小梅, 雷绍斌, 等. 碘塞罗宁联合肠内营养对腹腔感染合并低蛋白血症患者血清T3、T4和TSH及Th17水平的影响[J]. 热带医学杂志,2021,21(12):1572−1575,1584. [HU C Z, ZUO X M, LEI S B, et al. Effect of iodoseronin combined with enteral nutrition on serum T3, T4 and TSH and Th 17 levels in patients with abdominal infection with hypoproteinaemia[J]. The Journal of Tropical Medicine,2021,21(12):1572−1575,1584.] HU C Z, ZUO X M, LEI S B, et al. Effect of iodoseronin combined with enteral nutrition on serum T3, T4 and TSH and Th 17 levels in patients with abdominal infection with hypoproteinaemia[J]. The Journal of Tropical Medicine, 2021, 21(12): 1572−1575,1584.
[29] YAU M, JACOB M, ORTON S, et al. Perioperative stress dose steroid management of children with classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia:Too much or too little?[J]. Journal of Pediatric Urology, 2021, 17(5):654. e1-654. e6.
[30] FANG J, PAN W, WANG X Y, et al. Efficacy of stimulating Mingmen (GV4) and Guanyuan (CV4) on kidney deficiency in rat model:Laser irradiation traditional moxibustion[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,42(6):972−979.
[31] TSAI S F, HUNG H C, SHIH M M C, et al. High-fat diet-induced increases in glucocorticoids contribute to the development of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice[J]. The FASEB Journal,2021,36(1):e22130.
[32] 李继霞, 罗南萍, 公衍文, 等. 尿 17-OH、17-KS、VMA与血浆ALD、COR联合检测在肾上腺肿瘤中的诊断价值[J]. 实用医药杂志,2017,34(5):401−404. [LI J X, LUO N P, GONG Y W, et al. Diagnostic value of combining urinary 17-OH, 17-KS and VMA with plasma ALD and COR in adrenal tumors[J]. The Practical Medicine Journal,2017,34(5):401−404.] LI J X, LUO N P, GONG Y W, et al. Diagnostic value of combining urinary 17-OH, 17-KS and VMA with plasma ALD and COR in adrenal tumors[J]. The Practical Medicine Journal, 2017, 34(5): 401−404.
[33] MOHAMMAD D, MOHAMMADREZA N, KHADIJEH N, et al. Immunogenic evaluation of FMD virus immuno-dominant epitopes coupled with IL-2/FcIgG in BALB/c mice[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2019,132(1):30−37.
[34] TANG F, ZHONG Q, YANG Z R, et al. Low-dose cyclophosphamide combined with IL-2 inhibits tumor growth by decreasing regulatory T cells and increasing CD8+T cells and natural killer cells in mice[J]. Immunobiology,2022,227(3):152212. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152212
[35] QIN W, LUO H, YANG L, et al. Rubia cordifolia L. ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through dual inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathways[J]. Heliyon,2022,8(8):e10314. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10314
[36] 徐菲拉, 颜梅, 何忠平. 附子与人参配伍对心衰大鼠IL-10、IL-18、TNF-α表达水平的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2016,34(5):1233−1236. [XU F L, YAN M, HE Z P, et al. Effect of aconite and ginseng compatibility on the expression levels of IL-10, IL-18, and TNF-α in rats with heart failure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016,34(5):1233−1236.] XU F L, YAN M, HE Z P, et al. Effect of aconite and ginseng compatibility on the expression levels of IL-10, IL-18, and TNF-α in rats with heart failure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 34(5): 1233−1236.
[37] MATTOS B R, BONACIO G F, VITORINO T R, et al. TNF-α inhibition decreases MMP-2 activity, reactive oxygen species formation and improves hypertensive vascular hypertrophy independent of its effects on blood pressure[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,2020,180(8):114−121.
[38] 李苗苗, 崔华雷. 人参皂苷对重症腹腔感染大鼠肠黏膜萎缩及CRP、TNF-α和IL-6表达的影响[J]. 江苏医药,2019,45(2):113−115,104. [LI M M, CUI H L. Effect of ginsenosides on intestinal mucosal atrophy and expression of CRP, TNF-α and IL-6 in severe intraperitoneal-infected rats[J]. Jiangsu Medicine,2019,45(2):113−115,104.] LI M M, CUI H L. Effect of ginsenosides on intestinal mucosal atrophy and expression of CRP, TNF-α and IL-6 in severe intraperitoneal-infected rats[J]. Jiangsu Medicine, 2019, 45(2): 113−115,104.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
