Research Progress of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Separation and Purification of Natural Active Substances
-
摘要: 磁性分子印迹聚合物是将磁性纳米粒子与分子印迹聚合物组装而成的一类新型分离材料,具有选择性高、易分离和易再生的特点,可被用于食品、药品检测前处理以及天然活性物质的分离纯化等领域。本文介绍了磁性分子印迹技术的制备原理和方法,重点综述了近5年(2017~2022)磁性分子印迹聚合物在多酚类、生物碱、有机酸、萜类以及生物大分子化合物等天然活性物质的分离纯化方面的研究进展,并针对当前分离纯化领域的研究难点进行了讨论,以期为高值化、低含量的天然活性成分的富集、纯化及其分析检测提供研究参考。Abstract: Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers are novel separation materials assembled by magnetic nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymers, with specific selectivity, easy separation and regeneration, which can be used in the preliminary treatment of food and drugs, and the separation and purification of natural active substances. Herein, the preparation principle and method of magnetic molecular imprinting technology are elucidated, and the research progress (2017~2022) of magnetic molecular imprinting polymers in the separation and purification of natural active substances, such as polyphenols, alkaloids, organic acids, terpenoids, and macromolecules are reviewed. Meanwhile, the difficulties in the field of separation and purification are discussed. This review will provide reference for the enrichment, purification, analysis and detection of natural active substances.
-
药用植物中富含多种天然活性成分,如多酚类、黄酮类、多糖类、萜类、生物碱类等[1],具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤、降脂、降糖等多种生物活性[2]。然而,这些天然活性物质的分子往往结构复杂、异构体与同系物并存,含量低、基质效应强,使得分离纯化工作面临极大挑战[3]。现阶段,常用的分离纯化方法如大孔吸附树脂法[4]、离子交换纤维法[5]、β-环糊精键合固定相法[6]和聚酰胺柱层析吸附法[7]等,存在吸附容量小、选择性差、操作繁琐、分离效率低、大量使用有机溶剂等弊端[8]。为了获得高纯度的生物活性物质往往需要联合使用多种分离纯化方法,导致目标物的损耗增大,分离成本骤升[9]。分子印迹聚合物(Molecularly Imprinted Polymers,MIPs)是一种按照模板量身定做的多孔高分子吸附材料,具有选择性专一和吸附容量大等优势,在天然活性物质的分离纯化领域展现出优越的应用潜力[10]。将磁分离技术和分子印迹技术相结合制备得到的磁性分子印迹聚合物(Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers,MMIPs),不仅拥有MIPs所具备的可预定性和特异性,还具备超顺磁性和生物相容性,可通过外加磁场作用实现目标产物的分离,无需再使用离心、过滤等传统分离方式,有效降低了目标产物的损耗量。如今,MMIPs已在天然活性物质(如多酚、多糖、蛋白质)的分离纯化[11-12]、药物分析[13-14]、农残检测[15]和食品分析[16-17]等众多领域得到了广泛应用。
当前,大多数MMIPs是在有机溶剂体系中进行制备的,这样得到的MMIPs往往具有较强的“疏水记忆”,可以高效吸附有机相提取液中的活性物质,但对水相中的化合物的响应强度往往较弱 [18]。而自然界中生物活性物质的识别过程大多是在水相中进行,特别是多肽、蛋白质等生物大分子,为了排除非特异干扰,识别微环境最好与聚合微环境相一致,因此用于水相识别的印迹材料最好在水相中制备。近年来,研究者们相继在水相(或部分水相)中制备出了可在水相体系中保持较好的识别能力的亲水性磁性分子印迹聚合物(Hydrophilic Magnetic Molecule Imprinted Polymers,HMMIPs),大大拓宽了分子印迹聚合物的应用范围,对经济、生态及环境保护等方面具有重要意义[19-20]。基于此,本文意在通过介绍磁性分子印迹技术的制备原理和方法,重点综述近年来利用MMIPs分离纯化天然活性物质的应用研究进展,并对HMMIPs面临的技术难点进行分析讨论,以期为高值化、低含量的天然活性成分的富集、纯化及其分析检测提供研究参考。
1. 磁性分子印迹技术的概述
1998年,Mosbach等[21]利用悬浮聚合法制备了具有顺磁性及特异吸附性的悬浮磁微球,自此开创了磁性分子印迹技术。MMIPs的制备原理是利用表面分子印迹技术在纳米级磁性颗粒的表面合成聚合物层,聚合物层内孔穴的空间大小和功能基团的排布与模板分子高度契合,使得MMIPs兼具对模板分子的特异选择性和磁性颗粒自身的顺磁性,以实现模板分子的高效吸附和分离[22–24]。MMIPs的优势是能够在外加磁场作用下实现高效分离,选择性高,结构稳定性好,这使得磁性分子印迹技术成为天然活性物质分离纯化的重要手段之一[25]。Cheng等[26-27]先后在有机溶剂中制备了能够靶向吸附山奈酚和槲皮素的MMIPs,这两个聚合物具有特异的吸附性和较高的回收率,可在短时间内将目标化合物从苹果的甲醇提取液中分离出来。Chen等[28]利用沉淀聚合法制备了白藜芦醇的MMIPs,该聚合物磁化强度大,吸附能力强,可作为固相萃取吸附剂用于红酒中白藜芦醇含量测定的样品前处理。可见,MMIPs在活性物质的分离、纯化和含量测定等方面具有广阔的应用前景。
早期的MMIPs主要是在有机溶剂中制备得到的,为了提高MMIPs对水相中水溶性分子的高效识别和分离,研究者们尝试在水相中制备MMIPs,并应用于水溶性天然产物的分离和纯化,取得了较好的效果[29-30]。彭胜等[19]以绿原酸为模板分子,通过表面改性后合成了具有良好亲水性和磁固相萃取性能的亲水性磁性分子印迹树脂,结合磁固相萃取技术可实现复杂水体系样品中的绿原酸的高效分离富集。Li等[31]在Fe3O4@mSiO2的孔隙中制备了亲水性磁性分子印迹树脂,可实现对苯甲酸、没食子酸、原儿茶酸、香草酸、4-羟基苯甲酸、水杨酸和苯甲酸的特异性识别,并成功应用于水样中苯甲酸的检测。可见,HMMIPs能够实现对水相体系中目标模板分子的高效识别和吸附,未来可用于制备生物样品分离材料与仿生化学传感器等,在生物技术领域具有潜在的应用价值。
2. 磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备
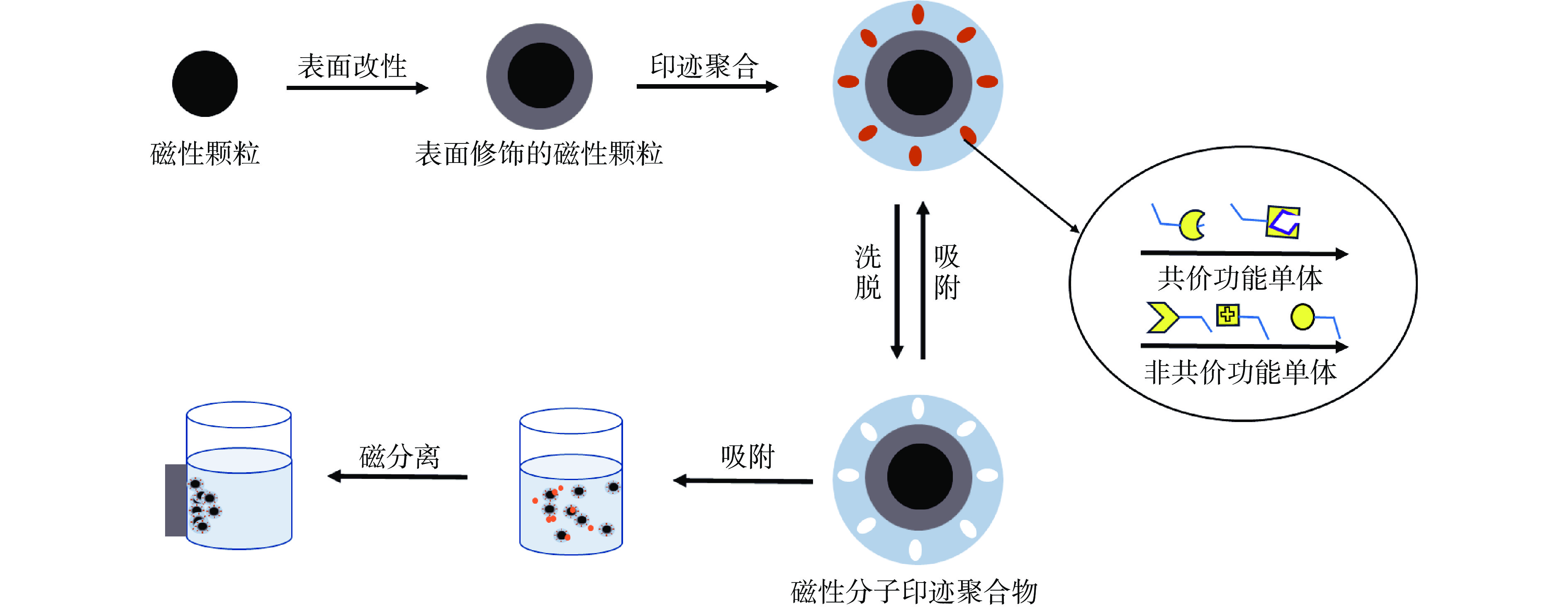
MMIPs的制备过程如图1所示,一般包括4个步骤:a. 制备具有优良磁响应性能的磁性粒子;b. 对磁性粒子表面进行功能化修饰;c. 在功能性磁性粒子表面进行分子印迹;d. 洗脱印迹层中的模板分子,从而获得表面具有特异识别位点的磁性分子印迹材料[32]。
2.1 磁性材料的选择
磁性纳米粒子是影响MMIPs制备成败的关键因素之一。目前已发现的磁性纳米材料主要是铁、钴、镍及其各自的氧化物或合金等,但镍和钴存在毒性,使其在生物、医药等领域中的应用受限[33]。因此,现在大多数研究是以低毒、稳定、价廉易得的Fe3O4作为制备MMIPs的磁性材料[34]。磁纳米颗粒的常用制备方法有溶剂热法[33]、共沉淀法[35]、微乳法[36]等。
2.2 磁性颗粒的表面修饰
一般来说,磁性纳米颗粒表面几乎没有可用于聚合反应的基团,需对其表面进行化学修饰,从而为后续印迹过程提供载体支撑。常用的修饰方法有表面活性剂的活化和硅烷偶联剂的硅烷化[37-38]等,例如,乙二醇和油酸可以作为表面活性剂更改聚合物的极性; 3-氨基丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES)或γ-甲基丙烯酰氧基丙基三甲氧基硅烷(MPS)可以在表面分别引入氨基[39]和乙烯基[40]等。
2.3 MMIPs的制备方法
制备MMIPs的常用方法有自由基聚合、溶胶-凝胶聚合和多巴胺自聚合等[41]。自由基聚合法可分为不可控自由基聚合以及可控自由基聚合。其中,常用的不可控的自由基聚合法主要有沉淀聚合、乳液聚合、悬浮聚合等;可控自由基聚合法包括原子转移自由基聚合(ATRP)和可逆加成断裂链转移(RAFT),各方法的优缺点的分析见表1。不难看出,现存方法大多存在表面洗脱难、大量使用有毒溶剂等弊病。为实现亲水性,HMMIPs的制备的方式有以下几种:一是采用水溶性功能单体制备,利用水溶性功能单体丙烯酰胺类和水溶性交联剂实现直接在水相中制备[42];二是采用溶胶-凝胶技术 [43-44];三是在水与有机相的混合体系中制备[45-46]。此外,表面印迹法[47-48]、分子印迹纳米线法[49]也是比较有效的制备方法。有研究者利用表面印迹法制备了能够吸附17β-雌二醇的亲水性纳米磁珠,实现了在水中对其进行靶向吸附[50];Zhou等[51]采用两步模板固定化方式与表面印迹技术相结合,首次制备了吸附氯酚的亲水磁性分子印迹树脂,可用于复杂环境水样中痕量氯酚的分离,为水环境污染检测提供了新的样品预处理材料。但是,目前可供选择的水溶性的功能单体和交联剂的种类较少,在一定程度上限制了HMMIPs的应用发展。
表 1 磁性分子印迹聚合物制备的常用方法Table 1. The common preparation methods of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers制备方法 优势 不足 首次报道 参考文献 悬浮聚合法 制备体系组成简单,影响因素可控性强,易操作 受水等极性强溶液影响较大,不适用于油性
模板分子,磁粒子包覆率低1998 [52-53] 乳液聚合法 粒径易控制,乳化剂可增强核-壳结构稳定性 表面活性剂影响材料形貌,去除步骤复杂 2002 [54-55] 溶胶-凝胶法 解决了大分子印迹过程中识别动力学慢的问题,适用于大分子物质印迹,形成的粒子形貌规整且单分散性较好 在粒子表面残留的硅烷偶联剂中疏水链段
会使粒子粘连2006 [56-57] 多巴胺自组装法 过程简单,聚合物具有良好的生物相容性和亲水性,多巴胺印迹壳层的厚度、聚合物的吸附容量和印迹效率可控 聚合时间长,具有毒性,涂层均匀性和稳定
性差,黏附力与沉积机理不清2007 [58-59] 沉淀聚合法 方法简单,无需添加分散剂 模板分子包埋深,洗脱难,传质慢,成本高 2009 [33] 原子转移自由基聚合法 广泛应用在固体表面接枝聚合物层 催化体系活性低,毒性大,催化剂的脱除较困难 2009 [60-61] 可逆加成断裂链转移 合成步骤少,无需使用金属催化剂 RAFT试剂需另外合成且气味难闻 2010 [62] 3. MMIPs在天然活性成分分离提取领域的应用
3.1 多酚类化合物
多酚类化合物是在植物中广泛分布的一类具有多个酚基团的化合物[63],已鉴定出约8000种,按结构可分为酚酸类、黄酮类、芪类和木酚素类等,具有抗炎、抗肿瘤、抗氧化等多种生物活性[64]。通常,多酚类化合物在植物中含量相对较低且结构相似,如同种植物内的黄酮类化合物存在众多母核相同、结构相似的衍生物,分离难度较大 [64-65]。例如,茶多酚中的儿茶素类化合物结构相似,尤其是表没食子酸儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)和其对映体没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(GCG),利用常规方法难以分离。Ma等[66]以儿茶素、表儿茶素和EGCG为模板分子,以低共熔溶剂(DES)为功能单体,制备了磁性分子印迹聚合物Fe3O4-CTS@DES-MIPs,并用于红茶中儿茶素、表儿茶素、EGCG的吸附,结果显示吸附后其含量分别为13.10、6.32、8.76 mg·g−1,其中儿茶素的回收率高达95.4%,可用于实际样品中生物活性物质的分离和含量测定。近年来,研究者们利用磁性分子印迹技术,陆续实现了从复杂基质中特异性地吸附芦丁[67]、橙皮素[40]、槲皮素[27]、山奈酚[68]等黄酮类化合物(见表2)。HMMIPs在多酚类化合物分离纯化领域的研究及应用主要集中在黄酮和酚酸类化合物,对芪类和木酚素类的相关报道较少,且大多研究是在有机相中实现目标化合物的靶向吸附[28]。因此,未来可以加大对芪类和木酚素类化合物的吸附研究,拓宽HMMIPs的应用范围。
表 2 磁性分子印迹聚合在天然活性成分分离提取中的应用Table 2. Application of magnetic molecular imprinting polymerization in separation and extraction of natural active substances化合物种类 样品 印迹样品 提取液溶剂 磁性纳米 参考文献 黄酮类化合物 果汁 芦丁 水 MGO/MHNTs@MIPs [67] 柑橘 橙皮素 乙醇/水 Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS [40] 红茶 儿茶素类 甲醇 Fe3O4-CTS@DES-MIPs [66] 苹果 槲皮素 甲醇/水 Fe3O4 [27] 银杏叶 山奈酚 甲醇 Fe3O4 [68] 生物碱化合物 地下水 吗啡、可待因、诺斯卡品、大麻碱、罂粟碱 水 MAA@Fe3O4 [73] 骆驼蓬 骆驼蓬碱 甲醇/水 Fe3O4@SiO2 [74] 黄连皮 黄连碱、小檗碱 水 UiO-66@PA@PEI@Fe3O4 [75] 有机酸化合物 杜仲黑茶 绿原酸 乙醇/水 Fe3O4@SiO2 [19] 黑茶 没食子酸 水 vinyl-Fe3O4@mSiO2 [81] 环境水样 水杨酸 水 Fe3O4@SiO2 [82] 菠菜、血样 草酸 甲醇/水 DES-Fe3O4 [83] 萜类化合物 栀子果 栀子苷 水 RAFT-Fe3O4@SiO2 [86] 雷公藤 南蛇藤素 甲醇/水 MCNTs [87] 生物大分子 松皮、松果 淀粉多糖 PBS缓冲液 Fe3O4@SiO2 [93-94] 全血 核酸 水(无酶) NpFeSiCl [95-96] 血清 胰岛素 Tris缓冲液 Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS [97] 血清 人血清白蛋白 Tris缓冲液 Fe3O4@CHO [98] 血清、尿液 尿磷蛋白 PBS缓冲液 Fe3O4@TiO2 [99] 3.2 生物碱类化合物
生物碱是植物次生代谢产物中的较大分支,种类丰富、结构复杂,多数有复杂的含氮杂环,具有抗肿瘤、抗炎、抗病毒、抗血小板凝集、抗心律失常以及抗高血压等作用,在卫生、医药等方面有着巨大的应用潜力[69-71]。然而,植物中生物碱的分离纯化难度较大,当前主要依赖于色谱法进行分离纯化,如薄层色谱、柱色谱、高效液相色谱等[72],但这些方法普遍存在耗时长、成本高、分离效果差等缺陷。例如,鸦片中的生物碱类物质结构相似,采用色谱技术对其进行分离效果并不理想。Nader等[73]利用表面印迹法制备得到的MMIPs可以从水中分别吸附吗啡、可待因、诺斯卡品、大麻碱、罂粟碱等,回收率在97%~102%,相对偏差均小于1.5%。此外,还有文献报道了应用MMIPs选择性提取富集水溶液中骆驼蓬碱[74]、黄连碱、小檗碱[75]等生物碱类化合物的工作。鉴于部分生物碱(如乌头碱等)对人体有害且易溶于水,可采用HMMIPs实现水相中有毒生物碱的靶向吸附和脱除,这为生物碱类化合物的脱除及痕量检测提供了新的思路和解决方案。
3.3 有机酸类化合物
有机酸广泛分布于植物根、叶、茎和果实中,包括苯甲酸、咖啡酸、没食子酸等芳香族有机酸,也包括柠檬酸、草酸、苹果酸、抗坏血酸、酒石酸等脂肪族有机酸[76]。目前工业生产有机酸通常采用生物发酵的方法,但存在产物少、纯度低、处理量大等问题[77]。如何快速提纯具有良好亲水性的有机酸化合物成为有机酸应用发展的突破点。常用的提纯方法包括沉淀法[78]、萃取法[79]、离子交换法[80]等,但是在纯化化合物的同时也伴随着分离效果差、处理复杂、环境污染等弊端[77]。近年相关研究发现,HMMIPs能够对水相中绿原酸[19]、没食子酸[81]、水杨酸[82]等芳香族有机酸进行特异性吸附。关于脂肪族有机酸,有研究者以三元DES(甜菜碱、柠檬酸和甘油)作为功能单体,制备了可测定菠菜和人体血液中草酸含量的MMIPs[83]。通过总结发现,目前研究者们对脂肪族有机酸相关研究相对较少,原因可能是相比于芳香族有机酸,脂肪族有机酸化合物与配体之间的分子间作用力相对较小,导致MMIPs制备成功率较低。综上可知,HMMIPs材料能够靶向吸附复杂体系中有机酸化合物,实现目标物质分离纯化,同时避免使用有机试剂,符合绿色化学的理念。
3.4 萜类化合物
环烯醚萜类化合物在药用植物中广泛分布,例如,植物体内的赤霉素、脱落酸等植物激素多为萜类化合物,具有抗癌、抗病毒、保肝利胆、保护心血管系统等生物活性,在生物医药领域具有广阔的应用前景[84],获得高纯度的萜类化合物对医药研究领域的发展具有重要价值。但是,常见的萜类化合物的分离纯化方法效果不佳,而且复杂操作也会导致损耗增大[85]。为此,有研究者利用可逆加成断裂链转移沉淀聚合法(RAFT)制备了亲水性磁性分子印迹微球,用于栀子黄色素和高纯度的栀子苷的提取分离[86];Li等[87]通过溶胶-凝胶法制备得到了能够从中药粗提物中吸附南蛇藤素的HMMIPs(见表2)。这些成果表明,MMIPs在萜类植物激素和药用成分的富集领域的应用潜能巨大。
3.5 生物大分子化合物
植物体内除含有大量小分子活性化合物外,还含有多糖、蛋白质和核酸等生物大分子活性物质[88],这些大分子本身稳定性较差,且所处的基质往往较为复杂,要获得高纯度且具有生物活性的大分子物质通常面临较大的挑战[89-90]。开发高效、温和,高选择性的生物大分子吸附分离材料是实现生物大分子物质分离纯化的有效途径。与其他生物大分子相比,制备吸附糖类化合物的MMIPs相对困难,主要是因为糖类化合物结构的长度、电荷、单糖序列等会发生不定向改变,需要采用复杂的方式来区分水中的糖类物质,这也导致利用MMIPs特异性分离糖类化合物的研究相对较少[91-92]。黄微薇等[93]制备了能够特异性吸附淀粉多糖的乙烯基双功能单体磁性分子印迹聚合微球,可以靶向吸附红松松皮粗多糖中多糖化合物;该团队还以淀粉为模板,在水溶液中成功合成了一种识别多糖的环氧功能化双功能MMIPs[94]。核酸的提取是分子检测中的重要步骤,有研究者制备了一种依托铁磁芯涂层介孔二氧化硅的核-壳结构的功能性纳米颗粒,利用特定氢键特异性吸附核酸,可有效避免蛋白质的污染[95];还有研究者通过表面有机卤化物功能化的磁性核壳纳米颗粒,实现对脱氧核糖核苷酸的提取[96]。相较于多糖和核酸,利用MMIPs分离纯化蛋白质的研究相对较多,且已经制备了能够快速靶向吸附胰岛素[97]、人血清白蛋白[98]、尿磷蛋白[99]等人体功能蛋白质的MMIPs。但是,关于蛋白质的空间效应、空间分布、表面构象等因素对其吸附过程的影响还有待深入研究。
4. 总结与展望
由于兼具高选择性和超顺磁性,且能实现水相中水溶性成分的分离和纯化,HMMIPs在多酚类、生物碱类、有机酸、萜类等小分子天然活性成分和蛋白质、多糖、核酸等生物大分子活性成分的分离纯化领域均得到了较好的应用,显示出广阔的应用前景。但是,HMMIPs也面临着功能单体的种类有限、精度低、再生性差、制备成功率低等诸多问题。因此,今后HMMIPs的研究工作应重点关注以下几个领域:a. 采用从已有的化合物中筛选、合成新的配体、接枝亲水基团等方法丰富亲水性功能单体,使其更适合于亲水性聚合反应;b. 使用多元功能单体制备具有多识别位点的HMMIPs,拓宽HMMIPs的适用范围,提高印迹精度,降低干扰作用;c. 优化制备流程、简化制备工艺,减少因多步反应导致的磁响应性能下降和颗粒团聚等问题;d. 加强对生物中间体的俘获和原位检测研究,为生物合成化学提供助力。
-
表 1 磁性分子印迹聚合物制备的常用方法
Table 1 The common preparation methods of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers
制备方法 优势 不足 首次报道 参考文献 悬浮聚合法 制备体系组成简单,影响因素可控性强,易操作 受水等极性强溶液影响较大,不适用于油性
模板分子,磁粒子包覆率低1998 [52-53] 乳液聚合法 粒径易控制,乳化剂可增强核-壳结构稳定性 表面活性剂影响材料形貌,去除步骤复杂 2002 [54-55] 溶胶-凝胶法 解决了大分子印迹过程中识别动力学慢的问题,适用于大分子物质印迹,形成的粒子形貌规整且单分散性较好 在粒子表面残留的硅烷偶联剂中疏水链段
会使粒子粘连2006 [56-57] 多巴胺自组装法 过程简单,聚合物具有良好的生物相容性和亲水性,多巴胺印迹壳层的厚度、聚合物的吸附容量和印迹效率可控 聚合时间长,具有毒性,涂层均匀性和稳定
性差,黏附力与沉积机理不清2007 [58-59] 沉淀聚合法 方法简单,无需添加分散剂 模板分子包埋深,洗脱难,传质慢,成本高 2009 [33] 原子转移自由基聚合法 广泛应用在固体表面接枝聚合物层 催化体系活性低,毒性大,催化剂的脱除较困难 2009 [60-61] 可逆加成断裂链转移 合成步骤少,无需使用金属催化剂 RAFT试剂需另外合成且气味难闻 2010 [62] 表 2 磁性分子印迹聚合在天然活性成分分离提取中的应用
Table 2 Application of magnetic molecular imprinting polymerization in separation and extraction of natural active substances
化合物种类 样品 印迹样品 提取液溶剂 磁性纳米 参考文献 黄酮类化合物 果汁 芦丁 水 MGO/MHNTs@MIPs [67] 柑橘 橙皮素 乙醇/水 Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS [40] 红茶 儿茶素类 甲醇 Fe3O4-CTS@DES-MIPs [66] 苹果 槲皮素 甲醇/水 Fe3O4 [27] 银杏叶 山奈酚 甲醇 Fe3O4 [68] 生物碱化合物 地下水 吗啡、可待因、诺斯卡品、大麻碱、罂粟碱 水 MAA@Fe3O4 [73] 骆驼蓬 骆驼蓬碱 甲醇/水 Fe3O4@SiO2 [74] 黄连皮 黄连碱、小檗碱 水 UiO-66@PA@PEI@Fe3O4 [75] 有机酸化合物 杜仲黑茶 绿原酸 乙醇/水 Fe3O4@SiO2 [19] 黑茶 没食子酸 水 vinyl-Fe3O4@mSiO2 [81] 环境水样 水杨酸 水 Fe3O4@SiO2 [82] 菠菜、血样 草酸 甲醇/水 DES-Fe3O4 [83] 萜类化合物 栀子果 栀子苷 水 RAFT-Fe3O4@SiO2 [86] 雷公藤 南蛇藤素 甲醇/水 MCNTs [87] 生物大分子 松皮、松果 淀粉多糖 PBS缓冲液 Fe3O4@SiO2 [93-94] 全血 核酸 水(无酶) NpFeSiCl [95-96] 血清 胰岛素 Tris缓冲液 Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS [97] 血清 人血清白蛋白 Tris缓冲液 Fe3O4@CHO [98] 血清、尿液 尿磷蛋白 PBS缓冲液 Fe3O4@TiO2 [99] -
[1] 周佳儒, 李久明, 徐宁, 等. 天然植物中有效成分的提取、分离技术研究进展[J]. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版),2018,33(1):14−18. [ZHOU J R, LI J M, XU N, et al. Progress in extraction and separation of effective components from natural plants[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Natural Sciences),2018,33(1):14−18. [2] 刘春秀. 植物活性成分的提取技术研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(3):1273−1274, 1277. [LIU C X. Research progress on extracting methods of effective constituent from plants[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(3):1273−1274, 1277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.03.007 [3] 王聪慧, 任娜, 魏微, 等. 天然产物分离纯化新技术[J]. 应用化工,2019,48(8):1940−1943. [WANG C H, REN N, WEI W, et al. New technology for separation and purification of natural products[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2019,48(8):1940−1943. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.08.039 [4] 杨敏, 张天锡, 史磊, 等. 大孔吸附树脂分离纯化中药成分影响因素探讨[J]. 中草药,2020,51(15):4050−4058. [YANG M, ZHANG T C, SHI L, et al. Review on factors influencing separation and purification of Chinese materia medica components by microporous adsorption resin[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2020,51(15):4050−4058. [5] 张志宏, 邢娜, 彭东辉, 等. 黄瓜子多糖的分离、纯化和体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国药房,2021,32(4):432−438. [ZHANG Z H, XING N, PENG D H, et al. Study on isolation, purification and in vitro antioxidant activity of the polysaccharides from Cucumis satiuus[J]. China Pharmacy,2021,32(4):432−438. [6] 邓利, 孙猛, 谭天伟, 等. β-环糊精键合固定相分离纯化银杏叶提取物和银杏黄酮[J]. 中草药,2004,35(10):1105−1109. [DENG L, SUN M, TAN T W, et al. Purification of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract and flavone on β-cyclodextrin-Superose 12 pg[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2004,35(10):1105−1109. [7] 孙一焱, 王菲, 臧彩娟, 等. 聚酰胺分离纯化金花葵花总黄酮的工艺研究[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报,2019,39(1):15−18. [SUN Y Y, WANG F, ZANG C J, et al. Separation and purification of total flavonoids from Flos Lonicerae by polyamide[J]. Journal of Liaoning Petrochemical University,2019,39(1):15−18. [8] 许苗苗, 王素素, 李辉, 等. 沉淀聚合法制备葛根素印迹微球及其固相萃取葛根粉[J]. 食品科学,2015(10):11−15. [XU M M, WANG S S, LI H, et al. Reparation of puerarin-imprinted polymer microspheres by precipitation polymerization technique for use in solid phase extraction of flavonoids from Pueraria root powder[J]. Food Science,2015(10):11−15. [9] 李秀凉, 杨涵冰, 吕莹, 等. 杏鲍菇多糖组分的分离纯化及结构鉴定[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(7):2097−2104. [LI X L, YANG H B, LÜ Y, et al. Isolation, purification and structural identification of Pleurotus eryngii polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(7):2097−2104. [10] 刘克建, 屈琦超. 分子印迹技术在天然活性成分分离纯化中的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(22):328−333, 340. [LIU K J, QU Q C. Research progress of separation and purification of the active ingredient of natural products based on molecular imprinted technology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(22):328−333, 340. [11] KASIRI E, HADDADI H, JAVADIAN H, et al. Highly effective pre-concentration of thymol and carvacrol using nano-sized magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on experimental design optimization and their trace determination in summer savoury, Origanum majorana and Origanum vulgare extracts[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2021,1182:122941. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122941
[12] 曹玉天, 盛万里, 齐小花, 等. 聚乙二醇修饰的槲皮素磁性分子印迹聚合物合成及其应用[J]. 分析科学学报,2021,37(6):719−725. [CAO Y T, SHENG W L, QI X H, et al. Synthesis and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers od PEG modified quercetin[J]. Journal of Analytical Science,2021,37(6):719−725. [13] 周晏曲, 方诗佩, 江如蓝, 等. 穿心莲内酯磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备及吸附性能考察[J]. 华西药学杂志,2022,37(2):126−129. [ZHOU Y Q, FANG S P, JIANG R L, et al. Preparation of andrographolide magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and investigation of its absorption properties[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2022,37(2):126−129. [14] MIRZAPOUR F, SADEGHI M. Magnetic molecular imprinted polymers for in vitro controlled release and solid-phase extraction of dextromethorphan: Synthesize, characterization, and application[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal,2022,31(5):553−571. doi: 10.1007/s13726-021-01003-x
[15] GUO T, WANG C, ZHOU H, et al. A multifunctional near-infrared fluorescent sensing material based on core-shell upconversion nanoparticles @ magnetic nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymers for detection of deltamethrin[J]. Microchimica Acta,2021,188(5):1−8.
[16] 马洁, 黄静, 曾延波, 等. 苏丹红 Ⅰ 磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备及其分离分析应用[J]. 分析测试学报,2013,32(6):726−731. [MA J, HUANG J, ZENG Y B, et al. Preparation of a kind of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer toward Sudan I and its application in separation of Sudan I[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2013,32(6):726−731. [17] 孙治安, 祁玉霞, 王霞, 等. 三聚氰胺磁性表面分子印迹聚合物的制备及其在牛奶样品中的应用[J]. 色谱,2018,36(8):716. [SUN Z A, QI Y X, WANG X, et al. Preparation of magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymers for melamine and its application in milk samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2018,36(8):716. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.03033 [18] 李随心, 霍云雷, 吴云鹏, 等. 亲水性丁香菌酯分子印迹微球的制备、表征与吸附性能的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(5):72−77, 92. [LI S X, HUO Y L, WU Y P, et al. Preparation, characterization and absorption properties of hydrophilic syringostrobin molecularly imprinted microspheres[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(5):72−77, 92. [19] 彭胜, 李奂, 施树云. 绿原酸亲水性磁性分子印迹树脂的合成及其固相萃取性能评价[J]. 色谱,2019,37(3):293−298. [PENG S, LI H, SHI S Y. Preparation of hydrophilic, magnetic molecularly imprinted resins of chlorogenic acid and evaluation of its solid-phase extraction performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2019,37(3):293−298. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.11026 [20] 张明明. 亲水印迹材料的制备及对天麻素和环烯醚萜苷的识别研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2017 ZHANG M M. Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of gastrodin and iridoid glycosides[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2017.
[21] ANSELL R J, MOSBACH K. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for drug radioligand binding assay[J]. Analyst,1998,123(7):1611−1616. doi: 10.1039/a801903g
[22] 李凯, 孙蕊, 彭羽, 等. Fe3O4 磁性分子印迹聚合物的研究进展[J]. 化学研究与应用,2015,27(12):1790−1795. [LI K, SUN R, PENG Y, et al. Research progress of Fe3O4 magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2015,27(12):1790−1795. [23] CARUSO F. Nanoengineering of particle surfaces[J]. Advanced Materials,2001,13(1):11−22. doi: 10.1002/1521-4095(200101)13:1<11::AID-ADMA11>3.0.CO;2-N
[24] 陈振羽, 郭亚甜, 张仪恒, 等. 磁性分子印迹技术在药物分析学创新实验中的应用[J]. 广州化工,2022,50(14):189−192, 203. [CHEN Z Y, GUO Y T, ZHANG Y H, et al. Application of magnetic molecular imprinting technique in innovative experiments of pharmaceutical analysis[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2022,50(14):189−192, 203. [25] 邓芳, 李越湘, 罗旭彪, 等. 磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备与研究进展[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程,2011,27(4):171−174. [DENG F, LI Y X, LUO X B, et al. Preparation and research progress of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering,2011,27(4):171−174. [26] CHENG Y, NIE J, LIU H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for effective extraction and determination of kaempferol from apple samples[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2020,1630:461531. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461531
[27] CHENG Y, NIE J, LI J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective recognition and determination of quercetin in apple samples[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,287:100−106. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.069
[28] CHEN F F, XIE X Y, SHI Y P. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective recognition of resveratrol in wine[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2013,1300:112−118. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.018
[29] DUAN F, CHEN C, ZHAO X, et al. Water-compatible surface molecularly imprinted polymers with synergy of bi-functional monomers for enhanced selective adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science: Nano,2016,3(1):213−222. doi: 10.1039/C5EN00198F
[30] HUANG J, TONG J, LUO J, et al. Green synthesis of water-compatible fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles for efficient detection of paracetamol[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(8):9760−9770.
[31] LI H, LONG R, TONG C, et al. Shell thickness controlled hydrophilic magnetic molecularly imprinted resins for high-efficient extraction of benzoic acids in aqueous samples[J]. Talanta,2019,194:969−976. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.099
[32] 胡颖. 磁性分子印迹材料的应用研究进展[J]. 浙江化工,2015,46(12):12−17. [HU Y. Advance in application of magnetic molecularly imprinted materials[J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry,2015,46(12):12−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4184.2015.12.004 [33] 陆彦蓉, 杨娅林, 殷晓阳, 等. 磁性纳米材料在兽药残留检测应用中的研究进展[J]. 中国兽药杂志,2022,56(2):88−93. [LU Y R, YANG Y L, YIN X Y, et al. Research progress of magnetic nanomaterials in veterinary drug residue detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug,2022,56(2):88−93. [34] 杨卫海, 吴瑶, 张轶, 等. 磁性分子印迹聚合物核壳微球的制备及应用[J]. 化学进展,2010,22(9):1819−1825. [YANG W H, WU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Preparation and application of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2010,22(9):1819−1825. [35] 黄莹. 溶剂热法制备高比表面积氮化碳及其对盐酸四环素的光降解性能研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2021 HUANG Y. Preparation of carbon nitride with high specific surface area bu solvothermal method and study on the photodegradation of tetracycline hydrochloride[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2021.
[36] 刘锋. 微乳法合成二氧化钛及其光催化去除一氧化氮性能研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2019 LIU F. Titanium dioxide prepared by microemulsion method and its photocatalytic removal of NO[D]. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2019.
[37] DODI G, HRITCU D, DRAGANESCU D, et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetically assisted patterned coatings[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2015,388:49−58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.04.011
[38] SU X, LI X, LI J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and determination of Rhodamine B in food[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,171:292−297. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.024
[39] FAROOQ S, NIE J, CHENG Y, et al. Synthesis of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective determination of imidacloprid in apple samples[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2019,42(14):2455−2465. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201900221
[40] WANG D D, GAO D, XU W J, et al. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective extraction of hesperetin from the dried pericarp of Citrus reticulata Blanco[J]. Talanta,2018,184:307−315. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.03.010
[41] 彭飞. 核壳型磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备表征及其对两种抗生素的吸附性能研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆师范大学, 2022 PENG F. Preparation characterization of core shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and their adsorption properties toward two antibiotics[D]. Wulumuqi: Xinjiang Normal University, 2022.
[42] 孙涛, 李媛媛, 张华承, 等. 基于环糊精的分子印迹技术[J]. 化学进展,2010,22(5):888. [SU T, LI Y Y, ZHANG H C, et al. Molecular imprinting technology based on cyclodextrins[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2010,22(5):888. [43] OLWILL A, HUGHES H, O’RIORDAIN M, et al. The use of molecularly imprinted sol-gels in pharmaceutical separations[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2004,20(6):1045−1050. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2004.04.029
[44] YANG D H, JU M J, MAEDA A, et al. Design of highly efficient receptor sites by combination of cyclodextrin units and molecular cavity in TiO2 ultrathin layer[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2006,22(3):388−392. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2006.06.013
[45] SUN H W, QIAO F X. Recognition mechanism of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and determination of nine quinolones in urine by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2008,1212(1−2):1−9. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.09.107
[46] YAN H, QIAO F, ROW K H. Molecularly imprinted-matrix solid-phase dispersion for selective extraction of five fluoroquinolones in eggs and tissue[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2007,79(21):8242−8248. doi: 10.1021/ac070644q
[47] GAO B, WANG J, YANG Y. Studies of imprinting conditions and application performance of pirimicarb molecule-imprinted material prepared using a novel surface-imprinting technique[J]. Chromatographia,2009,69(11):1353−1361.
[48] 陈志萍, 高保娇, 杨晓峰, 等. 表面印迹法制备胆红素分子印迹材料及其识别性能[J]. 过程工程学报,2009,9(2):387−392. [CHEN Z P, GAO B J, YANG X F, et al. Preparation of molecular surface imprinting material and its identification properties for bilirubin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2009,9(2):387−392. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2009.02.032 [49] LI Y, YANG H H, YOU Q H, et al. Protein recognition via surface molecularly imprinted polymer nanowires[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2006,78(1):317−320. doi: 10.1021/ac050802i
[50] TIAN X, SONG H, WANG Y, et al. Hydrophilic magnetic molecularly imprinted nanobeads for efficient enrichment and high performance liquid chromatographic detection of 17beta-estradiol in environmental water samples[J]. Talanta,2020,220:121367. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121367
[51] ZHOU T, WANG Y, LI T, et al. Fabricating magnetic hydrophilic molecularly imprinted resin with enhanced adsorption and recognition performance for targeted detecting chlorophenols in environmental water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,420:129904. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129904
[52] YE L. Synthetic strategies in molecular imprinting[J]. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Biotechnology,2015,150:1−24.
[53] HUANG C, WANG H, MA S, et al. Recent application of molecular imprinting technique in food safety[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2021,1657:462579. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462579
[54] WANG Z, ZHANG Z, YAN R, et al. Facile fabrication of snowman-like magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres for bisphenol A via one-step Pickering emulsion polymerization[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers,2021,164:104911. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.104911
[55] PAN J, ZHU W, DAI X, et al. Magnetic molecularly imprinted microcapsules derived from Pickering emulsion polymerization and their novel adsorption characteristics for λ-cyhalothrin[J]. RSC Advances,2014,4(9):4435−4443. doi: 10.1039/C3RA43178A
[56] LI G, ZHA J, NIU M, et al. Bifunctional monomer molecularly imprinted sol-gel polymers based on the surface of magnetic halloysite nanotubes as an effective extraction approach for norfloxacin[J]. Applied Clay Science,2018,162:409−417. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.06.003
[57] WANG B, DUAN A, XIE S, et al. The molecular imprinting of magnetic nanoparticles with boric acid affinity for the selective recognition and isolation of glycoproteins[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(41):25524−25529. doi: 10.1039/D1RA00716E
[58] WEI Q, CAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Preparation of surface molecularly imprinted poly (dopamine) film for 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4-BA) recognition by one-step method[J]. Analytical Letters,2011,44(10):1796−1806. doi: 10.1080/00032719.2010.526270
[59] LI H, JIANG B, LI J. Recent advances in dopamine-based materials constructed via one-pot co-assembly strategy[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2021,295:102489. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2021.102489
[60] LI X, PAN J, DAI J, et al. Surface molecular imprinting onto magnetic yeast composites via atom transfer radical polymerization for selective recognition of cefalexin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,198:503−511.
[61] KONG X J, ZHENG C, LAN Y H, et al. Synthesis of multirecognition magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer by atom transfer radical polymerization and its application in magnetic solid-phase extraction[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2018,410(1):247−257. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0716-9
[62] LI Y, LI X, CHU J, et al. Synthesis of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer by the surface RAFT polymerization for the fast and selective removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from aqueous solutions[J]. Environmental Pollution,2010,158(6):2317−2323. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.02.007
[63] 刘昕皓, 魏粉菊, 王学顺, 等. 多酚类化合物的生物活性研究进展[J]. 中国医药工业杂志,2021,52(4):471−483. [LIU X H, WEI F J, WANG X S, et al. Progress on biological activities of polyphenol[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceuticals,2021,52(4):471−483. [64] 刘军, 任汝全, 张燕如, 等. 五种黄酮类分子印迹分离技术研究及应用进展[J]. 化工进展,2019,38(7):3365−3376. [LIU J, REN R Q, ZHANG Y R, et al. Progress in research and application of five kinds of flavonoids molecular imprinting separation technique[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2019,38(7):3365−3376. [65] 陈亮, 李医明, 陈凯先, 等. 植物多酚类成分提取分离研究进展[J]. 中草药,2013,44(11):1501−1507. [CHEN L, LI Y M, CHENG K X, et al. Research progress in extraction and isolation of plant polyphenols[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2013,44(11):1501−1507. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2013.11.027 [66] MA W, DAI Y, ROW K H. Molecular imprinted polymers based on magnetic chitosan with different deep eutectic solvent monomers for the selective separation of catechins in black tea[J]. Electrophoresis,2018,39(15):2039−2046. doi: 10.1002/elps.201800034
[67] WANG F, NI X, ZHANG J, et al. Novel composite nanomaterials based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction and determination of rutin in fruit juice[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,381:132275. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132275
[68] LI X, DAI Y, ROW K H. Preparation of two-dimensional magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on boron nitride and a deep eutectic solvent for the selective recognition of flavonoids[J]. Analyst,2019,144(5):1777−1788. doi: 10.1039/C8AN02258E
[69] 刘志刚, 郭庆功, 陈景涛. 刺山柑总生物碱干预椎间盘退变模型大鼠髓核细胞的增殖与凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(11):1699. [LIU Z G, GUO Q G, CHEN J T. Effect of Capparis spinosa total alkaloid on proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in an intervertebral disc degeneration rat model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2021,25(11):1699. [70] 刘文成, 李琰, 常冰. 吡咯生物碱相关肝窦阻塞综合征发病机制的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2021,37(4):962−964. [LIU W C, LI Y, CHANG B. Research advances in the pathogenesis of pyrrole alkaloid-associated hepatic sinus obstruction syndrome[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology,2021,37(4):962−964. [71] 周贤春, 何春霞, 苏力坦, 等. 生物碱的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通讯,2006,17(3):476−479. [ZHOU X C, HE C X, SU L T, et al. Research progress on alkaloids[J]. Letters in Biotechnology,2006,17(3):476−479. [72] 张德华, 黄仁术, 左露, 等. 生物碱的提取方法研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源,2010,29(5):15−20. [ZHANG D H, HUANG R S, ZUO L, et al. Progress on the method of extraction of alkaloids[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources,2010,29(5):15−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2010.05.004 [73] NEMATI N, AHMADI S H, TABAR HEYDAR K. Simultaneous determination of five opium alkaloids in underground waters using molecularly imprinted polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticle based dispersive micro-solid phase extraction followed by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry,2021,101(1):1−17. doi: 10.1080/03067319.2019.1659253
[74] SADEGH N, ASFARAM A, JAVADIAN H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted solid phase microextraction-HPLC method based on Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2-molecularly imprinted polymer magnetic nano-sorbent for rapid and efficient extraction of harmaline from Peganum harmala extract[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2021,1171:122640. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122640
[75] WANG Y, YIN S, ZHAO C, et al. Preparation of a zirconium terephthalate metal-organic framework coated magnetic nanoparticle for the extraction of berberine prior to high-performance liquid chromatography analysis[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2021,44(6):1220−1230. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202001026
[76] 王兰兰, 宋晓卉, 杨笛, 等. 环境条件对植物有机酸影响研究进展[J]. 沈阳师范大学学报: 自然科学版,2019,37(3):236−239. [WANG L L, SONG X H, YANG D, et al. Progress of the effects of environmental conditions on organic acids in plants[J]. Journal of Shenyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2019,37(3):236−239. [77] 鄢凌, 傅宏鑫, 王旭东, 等. 生物基有机酸提取分离技术研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报,2018,18(1):1−10. [YAN L, FU H X, WANG X D, et al. Recent advances on recovery and separation of biomass-based organic acids[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2018,18(1):1−10. [78] DAN W, HAO C, JIANG L, et al. Efficient separation of butyric acid by an aqueous two-phase system with calcium chloride[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2010,18(4):533−537. doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(10)60255-8
[79] GAO M T, SHIMAMURA T, ISHIDA N, et al. Extractive lactic acid fermentation with tri-n-decylamine as the extractant[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,2009,44(5):350−354. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2008.12.001
[80] LIN S K C, DU C, BLAGA A C, et al. Novel resin-based vacuum distillation-crystallisation method for recovery of succinic acid crystals from fermentation broths[J]. Green Chemistry,2010,12(4):666−671. doi: 10.1039/b913021g
[81] WANG B, DENG H, WU M, et al. Magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres using gallic acid as a segment template for excellent recognition of ester catechins[J]. Analytical Methods,2018,10(27):3317−3324. doi: 10.1039/C8AY00903A
[82] ZHANG Z, NIU D, LI Y, et al. Magnetic, core-shell structured and surface molecularly imprinted polymers for the rapid and selective recognition of salicylic acid from aqueous solutions[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,435:178−186. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.033
[83] LI Y J, HE J Y, LI Q Y, et al. An edible molecularly imprinted material prepared by a new environmentally friendly deep eutectic solvent for removing oxalic acid from vegetables and human blood[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2022,414(7):2481−2491. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-03889-9
[84] 杜亚朋, 王美, 李璐遥, 等. 基于化合物稳定性探讨炮制对含环烯醚萜类成分中药药性及功效影响的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2021,52(16):5039−5051. [DU Y P, WANG M, LI L Y, et al. Research progress on effect of processing on properties and efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine containing iridoid terpenoids based on stability of compound[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(16):5039−5051. [85] 徐瑶, 徐树来, 刘志彬, 等. 灵芝三萜类化合物提取纯化及生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(11):458−464. [XU Y, XU S L, LIU Z B, et al. Research progress on the extraction, purification and biological activity of triterpenoids from the Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(11):458−464. [86] WANG J, YE Q, YU N, et al. Preparation of multiresponsive hydrophilic molecularly imprinted microspheres for rapid separation of gardenia yellow and geniposide from gardenia fruit[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,374:131610. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131610
[87] LI F, LI X, SU J, et al. A strategy of utilizing Cu2+-mediating interaction to prepare magnetic imprinted polymers for the selective detection of celastrol in traditional Chinese medicines[J]. Talanta,2021,231:122339. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122339
[88] ZHENG C, GAO R, ZHANG Y. Separation and recognition of biomacromolecule by molecular imprinting technique[J]. Se Pu= Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2006,24(3):309−314.
[89] ANDAÇ M, GALAEV I Y, DENIZLI A. Affinity based and molecularly imprinted cryogels: Applications in biomacromolecule purification[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2016,1021:69−80. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.09.034
[90] 孟姣姣. 低共熔溶剂绿色萃取技术用于生物大分子的分离分析研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2020 MENG J J. The research on deep eutectic solvent-based green extraction technology for the separation and analysis of biomacromolecules[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020.
[91] WANG C, GAO X, CHEN Z, et al. Preparation, characterization and application of polysaccharide-based metallic nanoparticles: A review[J]. Polymers,2017,9(12):689. doi: 10.3390/polym9120689
[92] CHANG B, ZHANG M, QING G, et al. Dynamic biointerfaces: From recognition to function[J]. Small,2015,11(9-10):1097−1112. doi: 10.1002/smll.201402038
[93] 黄微薇, 赵倩玉, 杨鑫, 等. 乙烯基功能化磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备和识别性能研究[J]. 功能材料,2019,50(1):1018−1025. [HUANG W W, ZHAO Q Y, YANG X, et al. Preparation and identification of viny functionalized magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2019,50(1):1018−1025. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2019.01.003 [94] 黄微薇, 赵倩玉, 杨鑫, 等. 环氧功能化双功能磁性分子印迹聚合物的合成及其在多糖吸附中的应用[J]. 色谱,2019,37(7):673−682. [HUANG W W, ZHAO Q Y, YANG X, et al. Synthesis and applications of epoxy-functionalized bi-functional magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for polysaccharide absorption[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2019,37(7):673−682. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2019.01018 [95] ALI T H, MANDAL A M, HEIDELBERG T, et al. Sugar based cationic magnetic core-shell silica nanoparticles for nucleic acid extraction[J]. RSC Advances,2022,12(22):13566−13579. doi: 10.1039/D2RA01139E
[96] ALI T H, MANDAL A M, HEIDELBERG T, et al. Ionic magnetic core-shell nanoparticles for DNA extraction[J]. RSC Advances,2020,10(64):38818−38830. doi: 10.1039/D0RA05933A
[97] GHEYBALIZADEH H, HEJAZI P. Influence of hydrophilic and hydrophobic functional monomers on the performance of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective recognition of human insulin[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers,2022,171:105152. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.105152
[98] CHEN F, MAO M, WANG J, et al. A dual-step immobilization/imprinting approach to prepare magnetic molecular imprinted polymers for selective removal of human serum albumin[J]. Talanta,2020,209:120509. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120509
[99] FANG X, WANG Z, SUN N, et al. Magnetic metal oxide affinity chromatography-based molecularly imprinted approach for effective separation of serous and urinary phosphoprotein biomarker[J]. Talanta,2021,226:122143. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122143





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
