Assessment of Amino Acid Nutrition in the Several Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Varieties from Fujian, China
-
摘要: 目的:探明5种福建名特花生果仁的氨基酸组成特征及营养价值差异。方法:以赖坊花生、衙口小琉球花生、朱口小籽花生、文亨红衣花生、洋后花生为试验材料,采用酸碱水解法,使用氨基酸自动分析仪测定花生果仁氨基酸含量。以WHO/FAO推荐的蛋白模式和鸡蛋蛋白标准模式为参照,计算并比较花生果仁的氨基酸评分(AAS)、化学评分(CS)和氨基酸比值系数分(SRC)。结果:5种花生果仁均至少含有18种蛋白质氨基酸,其总蛋白质含量为29.88~33.18 g/100 g。必需氨基酸、非必需氨基酸、酸味类氨基酸、甜味类氨基酸、苦味类氨基酸、儿童必需氨基酸、药用氨基酸、增香与着色氨基酸、抗菌氨基酸、伯氨基氨基酸、支链氨基酸、芳香族氨基酸含量分别为7.83~8.95、19.71~22.53、8.93~10.29、6.01~6.86、10.24~11.58、4.12~4.68、19.44~22.23、14.28~16.01、3.63~4.11、17.11~19.76、3.95~4.44、3.14~3.53 g/100 g。衙口小琉球花生的含量最高,显著高于除洋后花生外的其他花生品种(P<0.05)。氨基酸评分、化学评分和氨基酸比值系数分依次为24.29~28.29、37.58~43.67、41.61~45.70。色氨酸和苯丙氨酸+酪氨酸含量相对过剩,亮氨酸等7种氨基酸含量相对不足,其中含硫氨基酸为第一限制性氨基酸。结论:5种名特花生果仁的蛋白含量达到一级食用花生标准,氨基酸种类齐全,具有较大的开发利用价值。Abstract: Objective: The aim of this study is to investigate the amino acid nutrition of different peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) varieties from Fujian, China. Method: Laifang peanut, Yakou xiaoryukyu peanut, Zhukou small seed peanut, Wenheng Hongyi peanut and Yanghou peanut were selected as experimental materials. The composition of amino acids of peanut kernel was analyzed by an amino acid automatic analyzer after hydrolysis. Based on the obtained data , the amino acid nutrition value was evaluated according to egg protein model and the ideal model recommended by WHO/FAO. A series of indexes, including the amino acid score (AAS), chemical score (CS), and score of ratio coefficient of amino acid (SRC), were calculated. Results: At least 18 amino acids were found in these peanuts. The contents of protein in these peanuts varieties ranged from 29.88~33.18 g/100 g. The contents of essential amino acids, non-essential amino acids, sour amino acids, sweet amino acids, bitter amino acids, essential amino acids for child, medical amino acids, flavoring and coloring amino acids, anti-bacteria amino acids, primary amine amino acids, branched chain amino acids, and aromatic amino acids were 7.83~8.95, 19.71~22.53, 8.93~10.29, 6.01~6.86, 10.24~11.58, 4.12~4.68, 19.44~22.23, 14.28~16.01, 3.63~4.11, 17.11~19.76, 3.95~4.44 and 3.14~3.53 g/100 g, respectively. The highest values of these indexes were found in Yakou xiaoryukyu peanut, which were obviously higher than others except Yanghou peanut (P<0.05). The values of AAS, CS and SRC in these peanuts were 24.29~28.29, 37.58~43.67, and 41.61~45.70, respectively. The contents of Lys, Val, Ile, Leu, Thr, and (Met+Cys) in these peanuts were insufficient, while the contents of Trp, Phe and Tyr were relatively surplus. The firstly restrict amino acid was Met+Cys. Conclusion: The protein content of five famous and special peanut from Fujian reached the standard of first-class edible peanut in China, indicating that these five peanuts have great utilization value.
-
Keywords:
- peanut /
- protein /
- amino acid /
- nutrition
-
花生(Arachis hypogaea Linn.)又名“长生果”、“泥豆”,富含蛋白质、脂肪、糖类物质和维生素等,脂肪含量为44%~45%,蛋白含量为24%~36%,是我国广泛食用的坚果之一[1-3]。食物蛋白质营养价值主要取决于氨基酸的种类及含量[4]。研究表明,氨基酸是影响花生食用品质尤其是炒花生风味的重要前体物质,其中天门冬氨酸(Asp)、谷氨酸(Glu)等更是直接影响炒花生的典型风味[5]。因此,评价不同花生品种蛋白氨基酸营养价值,可为花生品种选育和开发利用提供参考依据。
目前,关于不同品种农作物的氨基酸营养评价进行了大量研究。Martínez-Gil等[6]比较了小维多等4种葡萄的氨基酸营养,并分析了氨基酸含量差异对酿酒的影响。Syafutri等[7]研究了不同稻米品种间的蛋白、氨基酸、必需氨基酸含量差异及其对烹饪时间的影响。孙娟娟等[8]对6个我国紫花苜蓿品种的氨基酸营养进行了评价,发现紫花苜蓿氨基酸种类齐全,营养价值接近理想氨基酸标准,且具有一定的药用价值,但品种间的药效氨基酸、风味氨基酸含量等指标有所差异。赵凤敏等[9]研究发现,氨基酸营养的差异将直接影响马铃薯的功效、口感、气味,但不同品种花生的氨基酸营养研究尚不多见。
花生种植面积位居福建大田作物第三位,地方特色品种众多,其中较为知名的有赖坊花生、衙口小琉球花生等。本研究以赖坊花生、衙口小琉球花生、朱口小籽花生、文亨红衣花生、洋后花生等5种福建地方特色花生为研究对象,分析蛋白氨基酸组成,采用国际通用的氨基酸评价方法比较其营养价值,以期为花生品种选育及相关食品开发提供数据支撑。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
供试花生品种如表1所示 样品均为7月份采摘、果皮颜色由白转深、饱满度高的果实,自然晒干,去壳,果仁粉碎,称取样品、移入滤纸筒内、索氏抽提6~10 h后风干、混匀待测。氨基酸标准品(2.5 μmol/mL,≥99%) Sigma公司;色氨酸标准品(≥99%) 上海嘉辰化工有限公司;柠檬酸、柠檬酸钠、氯化钠、氢氧化钠、无水乙醇、盐酸、硫酸和硼酸(优级纯),其余试剂均为分析纯 上海国药集团。
表 1 样品来源Table 1. Source of samples编号 名称 来源 P1 赖坊花生 三明市清流县 P2 衙口小琉球花生 泉州市晋江市 P3 朱口小籽花生 三明市泰宁县 P4 文亨红衣花生 龙岩市连城县 P5 洋后花生 南平市延平区 LA8080型氨基酸自动分析仪 日本HITACHI公司;Kjeltec 2300型全自动凯氏定氮仪 瑞典FOSS TECATOR公司;DHG-9140A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蛋白质含量测定
参考GB 5009.5-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定[10]。
1.2.2 氨基酸组成测定
色氨酸:称取0.2~0.3 g试样,置于聚四氟乙烯衬管中,加入1.5 mL 4 mol/L氢氧化锂,置液氮中冷冻后,将衬管放入水解管,抽真空封管,在(110±1)℃恒温干燥箱中,水解20 h,冷却至室温,破口,移至25 mL容量瓶中,加入6 mol/L盐酸中和,用pH 2.2柠檬酸钠缓冲液稀释定容,4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液待测。
其它氨基酸:参考GB 5009.124-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[11]。
1.2.3 氨基酸营养评价
以鸡蛋蛋白为标准蛋白,以WHO/FAO氨基酸参考模式为评价标准进行氨基酸营养评价。氨基酸评分(Amino acid score,AAS)、化学评分(Chemical Score,CS)、氨基酸比值(Amino acid ratio,RC)、氨基酸比值系数(Amino acid ratio coefficient,RCAA)和氨基酸比值系数分(Amino acid ratio coefficient score,SRC)等参数的计算参考文献[12-13]。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据用Excel 2007和SPSS 17.0软件进行统计分析,结果以
¯X±S 表示,利用单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA)检验差异显著性、邓肯式新复极差法(Duncan’s multiple range test)作多重比较分析和双变量相关系数(Pearson)进行相关性分析。2. 结果和分析
2.1 氨基酸含量及其种类
氨基酸是组成蛋白质的基本单位,是生命活动的基础物质,且是影响食物营养品质的重要指标之一[14]。5个花生品种果仁中的蛋白质含量、氨基酸组成如表2所示。由于天冬酰胺(Asn)和谷氨酰胺(Gln)在酸处理下会分解并生成天门冬氨酸(Asp)和谷氨酸(Glu),故5个花生品种至少含有18种蛋白质氨基酸,包括8种必需氨基酸和10种非必需氨基酸。供试花生品种果仁中蛋白质含量介于29.88~33.18 g/100 g,优于榛子、杏仁等坚果类,P2还高于南瓜、西瓜子仁等种子类[15],组间差异显著(P<0.05);必需氨基酸、非必需氨基酸、氨基酸总量分别为7.83~8.95、19.71~22.53、27.54~31.47 g/100 g,P2最高,P1最低,但均高于黑花生和桂花红等花生品种和纸皮核桃、东北松子、开心果等坚果[16-17]。可见,花生蛋白质含量丰富,氨基酸种类齐全,优于大部分坚果类产品,但品种间含量差异明显。
表 2 花生果仁中蛋白质氨基酸含量(n=3, g/100 g)Table 2. The contents of protein and amino acids in peanut kernels (n=3, g/100 g)氨基酸 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 异亮氨酸Ile* 0.93±0.04c 1.08±0.00a 0.97±0.02b 0.98±0.03b 1.05±0.02a 亮氨酸Leu* 1.83±0.06b 2.05±0.01a 1.87±0.04b 1.87±0.05b 2.04±0.05a 赖氨酸Lys* 0.93±0.03c 1.17±0.02a 1.05±0.01b 1.05±0.04b 1.15±0.03a 胱氨酸Cys△ 0.33±0.03b 0.34±0.01a 0.36±0.00a 0.35±0.01a 0.37±0.03a 蛋氨酸Met* 0.13±0.01b 0.15±0.02a 0.17±0.01a 0.15±0.03a 0.16±0.02a 酪氨酸Tyr△ 1.10±0.06b 1.23±0.02a 1.13±0.02b 1.12±0.04b 1.20±0.04a 苯丙氨酸Phe* 1.47±0.02b 1.60±0.04a 1.49±0.04b 1.48±0.05b 1.57±0.04a 苏氨酸Thr* 0.78±0.02c 0.88±0.01a 0.81±0.02b 0.82±0.02b 0.84±0.02a 色氨酸Trp* 0.57±0.04b 0.70±0.02a 0.64±0.02a 0.66±0.02a 0.68±0.02a 缬草氨酸Val* 1.19±0.04b 1.32±0.01a 1.21±0.03b 1.23±0.04b 1.23±0.04b 组氨酸His△ 0.67±0.02b 0.75±0.01a 0.68±0.02b 0.68±0.02b 0.72±0.01a 精氨酸Arg△ 3.45±0.09b 3.94±0.07a 3.53±0.10b 3.48±0.10b 3.88±0.015a 天门冬氨酸Asp△ 3.39±0.64b 3.83±0.06a 3.47±0.08b 3.48±0.10b 3.76±0.05a 丝氨酸Ser△ 1.43±0.06c 1.61±0.02a 1.50±0.03b 1.51±0.04b 1.58±0.02a 谷氨酸Glu△ 5.88±0.13b 6.46±0.07a 6.03±0.12b 6.03±0.17b 6.48±0.10a 脯氨酸Pro△ 1.09±0.04c 1.29±0.04a 1.16±0.01b 1.20±0.04b 1.24±0.04a 丙氨酸Ala△ 1.12±0.03b 1.27±0.02a 1.13±0.02b 1.16±0.04b 1.24±0.02a 甘氨酸Gly△ 1.59±0.02c 1.81±0.04a 1.73±0.04b 1.68±0.07b 1.86±0.04a 必需氨基酸EAA 7.83±0.20c 8.95±0.06a 8.21±0.16b 8.24±0.27b 8.74±0.07a 非必需氨基酸NEAA 19.71±0.97b 22.53±0.21a 20.72±0.41b 20.68±0.63b 22.33±0.36a 氨基酸总量TAA 27.54±1.16b 31.47±0.27a 28.93±0.57b 28.92±0.90b 31.07±0.42a 蛋白质CP 29.88±0.08e 33.18±0.15a 30.53±0.12c 30.16±0.12d 32.13±0.05b 注:*EAA必需氨基酸;△NEAA非必需氨基酸;TAA氨基酸总量;CP蛋白质;同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),表4同。 花生果仁的Glu含量最高,其次为精氨酸(Arg)、天门冬氨酸(Asp)和亮氨酸(Leu),四者共占氨基酸总量的51.38%~52.01%,与石太渊等的研究结果相一致[15,18],P2和P5组间差异不显著(P>0.05),但均显著高于其他组(P<0.05)。色氨酸(Trp)、含硫氨基酸(胱氨酸(Cys)+蛋氨酸(Met))含量较低,P1显著低于其他组(P<0.05)。单一氨基酸含量排序与林茂等[16]的研究结果相近。关于单一氨基酸的生理功效,已有大量的研究,如Glu具有健脑益智、保肝护肝的作用;Arg具有提高抗氧化能力、增强免疫力、改善心脑血管等生理功能;Asp具有增强肝功、解除氨中毒、保护心肌的作用;Leu具有调节蛋白合成与分解、防治肝、肾功能衰竭、刺激胰岛素分泌等功能[19]。
2.2 呈味氨基酸含量及组成
烹饪或加工可使食物的蛋白质降解为短肽和氨基酸,从而获得风味独特、味道鲜美的食用品质[20]。5个花生品种果仁中的呈味氨基酸含量如表3所示,可知均至少含有2种酸味类氨基酸、5种甜味类氨基酸和8种苦味类氨基酸。5个花生品种果仁中酸味类、甜味类以及苦味类氨基酸含量分别为8.93~10.29、6.01~6.86、10.24~11.58 g/100 g,分别占氨基酸总量的32.44%~32.99%、21.78%~22.03%、36.39%~37.17%,高于黑花生、杏仁、扁桃仁、纸皮核桃等坚果[17,21]。其中,P2的含量最高,P1的含量最低,P2和P5组间差异均不显著(P>0.05),而显著高于其他组(P<0.05)。可见,花生在食品调味工业上具有良好的应用前景。
表 3 花生果仁中呈味氨基酸含量Table 3. The contents of flavor amino acids in peanut kernels品种 SOAA SWAA BIAA SOAA/TAA SWAA/TAA BIAA/TAA g/100 g % P1 8.93±0.70b 6.01±0.16c 10.24±0.24b 32.44 21.81 37.17 P2 10.29±0.10a 6.86±0.10a 11.58±0.13a 32.69 21.81 36.79 P3 9.50±0.19b 6.33±0.09b 10.57±0.28b 32.84 21.87 36.54 P4 9.51±0.26b 6.37±0.21b 10.52±0.34b 32.90 22.03 36.39 P5 10.25±0.15a 6.77±0.09a 11.34±0.19a 32.99 21.78 36.49 注:SOAA酸味类氨基酸:Asp、Glu;SWAA甜味类氨基酸:Thr、Ala、Gly、Pro、Ser;BIAA苦味类氨基酸:Ile、Leu、Met、Phe、Trp、Val、His、Arg;同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.3 特殊功效氨基酸含量及组成
氨基酸不仅在食品的呈味方面发挥着重要作用,而且是维系人体生命活动的重要物质,具有各种生理功能。5个花生品种果仁中的儿童必需氨基酸、药用氨基酸、增香与着色氨基酸、抗菌氨基酸、伯氨基氨基酸、支链氨基酸、芳香族氨基酸等特殊功效氨基酸含量如表4所示,含量最高的均为P2,P1含量最低,P2和P5组间差异均不显著(P>0.05),但显著高于其他组(P<0.05)。其中,果仁中增香与着色氨基酸、抗菌氨基酸、伯氨基氨基酸含量分别为14.28~16.01、3.63~4.11、17.11~19.76 g/100 g,远高于黑花生、杏仁、开心果等坚果[17,21]。增香与着色氨基酸的氨基可与还原糖的羰基产生美拉德反应生成具有愉快香味的褐色物质,促进食品的增香与着色;一定浓度的抗菌氨基酸会对引起食品腐败的微生物产生抑制作用;伯胺基氨基酸替代仲胺与亚硝酸盐产生范斯莱克反应生成氮气和有机酸,抑制二甲氨基亚硝胺的生成[19]。
表 4 花生果仁中特殊功效氨基酸含量Table 4. The content of special functional amino acids in peanut kernels氨基酸 单位 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 CE g/100 g 4.12±0.10b 4.68±0.07a 4.21±0.12b 4.15±0.12b 4.59±0.15a MAA 19.44±0.91b 22.23±0.18a 20.46±0.42b 20.34±0.64b 22.10±0.40a FCAA 14.28±0.34b 16.01±0.06a 14.72±0.31b 14.68±0.42b 15.87±0.30a ABAA 3.63±0.06c 4.11±0.08a 3.86±0.10b 3.81±0.14b 4.10±0.07a PAAA 17.11±0.86c 19.76±0.16a 18.09±0.33b 18.08±0.54b 19.61±0.33a BCAA 3.95±0.12b 4.44±0.01a 4.05±0.10b 4.08±0.12b 4.33±0.05a AAA 3.14±0.09b 3.53±0.08a 3.26±0.08b 3.26±0.12b 3.45±0.08a CE/TAA % 14.96 14.88 14.55 14.36 14.78 MAA/TAA 70.60 70.64 70.72 70.32 71.13 FCAA/TAA 51.85 50.89 50.89 50.75 51.09 ABAA/TAA 13.17 13.05 13.35 13.19 13.24 PAAA/TAA 62.15 62.79 62.54 62.52 63.13 BCAA/AAA 125.93 125.76 124.11 125.38 125.29 BCAA/EAA 50.45 49.64 49.31 49.58 49.52 注:CE儿童必需氨基酸:His、Arg;MAA药用氨基酸:Asp、Glu、Gly、Met、Leu、Phe、Tyr、Lys、Arg;FCAA增香与着色氨基酸:Glu、Cys、Val、Leu、Lys、His、Arg;ABAA抗菌氨基酸:Phe、Trp、Gly;PAAA伯胺基氨基酸:Asp、Glu、Pro、Gly、Ala、Lys、Arg;BCAA支链氨基酸:Ile、Leu、Val;AAA芳香族氨基酸:Phe、Tyr、Trp。 果仁中药用氨基酸含量为19.44~22.23 g/100 g,占氨基酸总量的70.32%~71.13%,远高于黑花生、杏仁、扁桃仁、开心果等坚果[17,21],也高于石斛[22]、人参[23]、冬虫夏草[24]、枸杞[25]等中药材,P5的占比高达71%以上。Glu、Arg、Asp、Leu等9种药用氨基酸,在一般植物中含量少,有些人体不能合成,是维持机体氮平衡所必需的[19]。可见,花生具有很高的药用价值,在保健食品方面有广阔的开发前景。
果仁中儿童氨基酸、支链氨基酸、芳香族氨基酸含量分别为4.12~4.68、3.95~4.44、3.14~3.53 g/100 g,均高于黑花生、杏仁、开心果等坚果[17,21];支链氨基酸占必需氨基酸总量的49.31%~50.45%,低于桂花红花生、杏仁、东北榛子、夏威夷果等坚果[17,21]。支链氨基酸是糖类、脂肪缺乏或代谢障碍时重要的能源物质,具有调节蛋白合成与分解、调节芳香族氨基酸进入血脑屏障和防治肝肾功能衰竭等功能,分别占成人、儿童及婴儿每日EAA需要量的40%、41%及45%[19]。可见,花生能够满足人体对支链氨基酸的需求。
2.4 氨基酸营养价值评价
食物蛋白质营养价值的高低主要取决于必需氨基酸的种类、含量及组成比例。5个花生品种果仁、鸡蛋蛋白和FAO/WHO标准模式的每克氮中必需氨基酸的毫克数(氨基酸含量×62.5/蛋白质的百分含量)如表5所示,花生果仁中必需氨基酸总量为1937~2069 mg/g N,P5的含量最高,P1的含量最低,均低于鸡蛋蛋白、FAO/WHO标准模式;E/T、E/N分别为33.17%~33.63%、49.64%~50.67%,均低于瓜子、大果榛子、纸皮核桃和东北松子等坚果、鸡蛋蛋白和FAO/WHO标准模式,而高于诸暨香榧等11种坚果[17,21]。根据标准模式,花生蛋白的必需氨基酸组成比例不理想,营养价值略低。
表 5 花生果仁中必需氨基酸含量与鸡蛋蛋白、FAO/WHO标准模式的比较(mg/g N)Table 5. The composition of essential amino acid in peanut kernels and comparison with egg’s protein and FAO/WHO standard model (mg/g N)氨基酸 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 鸡蛋蛋白 FAO/WHO Ile 195 203 199 204 211 331 250 Leu 384 385 382 388 410 534 440 Lys 195 220 214 217 231 441 340 Met+Cys 96 94 109 103 107 386 220 Phe+Tyr 538 534 536 539 556 565 380 Thr 164 166 165 170 169 292 250 Trp 119 131 132 136 137 106 60 Val 248 248 248 254 248 411 310 TEAA 1937 1982 1986 2011 2069 3066 2250 E/T(%) 33.63 33.43 33.53 33.55 33.17 49.80 36.35 E/N(%) 50.67 50.21 50.44 50.49 49.64 99.22 57.11 化学分析法是评定食物蛋白质营养价值的常用方法。不同参考蛋白模式评价结果差距较大,SRC以FAO/WHO作为理想蛋白参考模式,AAS、CS以全蛋蛋白作为理想蛋白参考模式。5种花生品种果仁的RC、RCAA、SRC、AAS和CS的评分如表6示,果仁中SRC为41.61~45.70,评分最高的为P1,最低的为P4,Leu、Val、Ile、Thr、Lys、Met+Cys的RC值均小于1,表现严重不足,为限制性氨基酸,Trp、Phe+Tyr的RC值均大于1,表示相对过剩;果仁中AAS、CS分别为24.29~28.29、37.58~43.67,评分最高的均为P3,最低的均为P2,Met+Cys为第一限制性氨基酸。根据蛋白质互补法,建议与Met+Cys相对过剩的金针菇[26]或Phe+Tyr相对缺乏的松露[27]等食物搭配,提高机体对蛋白质的利用率。
表 6 花生仁中必需氨基酸营养价值评分Table 6. Nutritional scores of essential amino acids in peanut kernels品种 RC、
RCAAFAO/WHO Egg protein Ile Leu Lys Met+Cys Phe+Tyr Thr Trp Val SRC AAS* CS* P1 RC 0.78 0.87 0.57 0.44 1.41 0.66 1.98 0.80 45.70 24.93 39.46 RCAA 0.83 0.93 0.61 0.47 1.51 0.70 2.11 0.85 P2 RC 0.81 0.88 0.65 0.43 1.41 0.67 2.19 0.80 42.30 24.29 37.58 RCAA 0.83 0.90 0.66 0.44 1.44 0.68 2.24 0.82 P3 RC 0.80 0.87 0.63 0.50 1.41 0.66 2.20 0.80 42.93 28.29 43.67 RCAA 0.81 0.88 0.64 0.51 1.44 0.67 2.23 0.81 P4 RC 0.82 0.88 0.64 0.47 1.42 0.68 2.27 0.82 41.61 26.66 40.66 RCAA 0.82 0.88 0.64 0.47 1.42 0.68 2.27 0.82 P5 RC 0.85 0.93 0.68 0.49 1.46 0.68 2.29 0.80 42.58 27.74 41.10 RCAA 0.83 0.91 0.67 0.48 1.43 0.66 2.24 0.78 注:*表示第一限制氨基酸为Met+Cys。 3. 结论
根据NY/T 1067-2006食用花生标准判定,赖坊花生、衙口小琉球花生、朱口小籽花生、文亨红衣花生、洋后花生等5个福建地方特色花生品种果仁蛋白质含量达29.88~33.18 g/100 g,达到一级食用花生标准。花生蛋白质氨基酸种类齐全,不同花生品种蛋白质氨基酸组成特征各异,必需氨基酸组成不均衡,建议在饮食中与食用菌等食物搭配食用。
-
表 1 样品来源
Table 1 Source of samples
编号 名称 来源 P1 赖坊花生 三明市清流县 P2 衙口小琉球花生 泉州市晋江市 P3 朱口小籽花生 三明市泰宁县 P4 文亨红衣花生 龙岩市连城县 P5 洋后花生 南平市延平区 表 2 花生果仁中蛋白质氨基酸含量(n=3, g/100 g)
Table 2 The contents of protein and amino acids in peanut kernels (n=3, g/100 g)
氨基酸 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 异亮氨酸Ile* 0.93±0.04c 1.08±0.00a 0.97±0.02b 0.98±0.03b 1.05±0.02a 亮氨酸Leu* 1.83±0.06b 2.05±0.01a 1.87±0.04b 1.87±0.05b 2.04±0.05a 赖氨酸Lys* 0.93±0.03c 1.17±0.02a 1.05±0.01b 1.05±0.04b 1.15±0.03a 胱氨酸Cys△ 0.33±0.03b 0.34±0.01a 0.36±0.00a 0.35±0.01a 0.37±0.03a 蛋氨酸Met* 0.13±0.01b 0.15±0.02a 0.17±0.01a 0.15±0.03a 0.16±0.02a 酪氨酸Tyr△ 1.10±0.06b 1.23±0.02a 1.13±0.02b 1.12±0.04b 1.20±0.04a 苯丙氨酸Phe* 1.47±0.02b 1.60±0.04a 1.49±0.04b 1.48±0.05b 1.57±0.04a 苏氨酸Thr* 0.78±0.02c 0.88±0.01a 0.81±0.02b 0.82±0.02b 0.84±0.02a 色氨酸Trp* 0.57±0.04b 0.70±0.02a 0.64±0.02a 0.66±0.02a 0.68±0.02a 缬草氨酸Val* 1.19±0.04b 1.32±0.01a 1.21±0.03b 1.23±0.04b 1.23±0.04b 组氨酸His△ 0.67±0.02b 0.75±0.01a 0.68±0.02b 0.68±0.02b 0.72±0.01a 精氨酸Arg△ 3.45±0.09b 3.94±0.07a 3.53±0.10b 3.48±0.10b 3.88±0.015a 天门冬氨酸Asp△ 3.39±0.64b 3.83±0.06a 3.47±0.08b 3.48±0.10b 3.76±0.05a 丝氨酸Ser△ 1.43±0.06c 1.61±0.02a 1.50±0.03b 1.51±0.04b 1.58±0.02a 谷氨酸Glu△ 5.88±0.13b 6.46±0.07a 6.03±0.12b 6.03±0.17b 6.48±0.10a 脯氨酸Pro△ 1.09±0.04c 1.29±0.04a 1.16±0.01b 1.20±0.04b 1.24±0.04a 丙氨酸Ala△ 1.12±0.03b 1.27±0.02a 1.13±0.02b 1.16±0.04b 1.24±0.02a 甘氨酸Gly△ 1.59±0.02c 1.81±0.04a 1.73±0.04b 1.68±0.07b 1.86±0.04a 必需氨基酸EAA 7.83±0.20c 8.95±0.06a 8.21±0.16b 8.24±0.27b 8.74±0.07a 非必需氨基酸NEAA 19.71±0.97b 22.53±0.21a 20.72±0.41b 20.68±0.63b 22.33±0.36a 氨基酸总量TAA 27.54±1.16b 31.47±0.27a 28.93±0.57b 28.92±0.90b 31.07±0.42a 蛋白质CP 29.88±0.08e 33.18±0.15a 30.53±0.12c 30.16±0.12d 32.13±0.05b 注:*EAA必需氨基酸;△NEAA非必需氨基酸;TAA氨基酸总量;CP蛋白质;同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),表4同。 表 3 花生果仁中呈味氨基酸含量
Table 3 The contents of flavor amino acids in peanut kernels
品种 SOAA SWAA BIAA SOAA/TAA SWAA/TAA BIAA/TAA g/100 g % P1 8.93±0.70b 6.01±0.16c 10.24±0.24b 32.44 21.81 37.17 P2 10.29±0.10a 6.86±0.10a 11.58±0.13a 32.69 21.81 36.79 P3 9.50±0.19b 6.33±0.09b 10.57±0.28b 32.84 21.87 36.54 P4 9.51±0.26b 6.37±0.21b 10.52±0.34b 32.90 22.03 36.39 P5 10.25±0.15a 6.77±0.09a 11.34±0.19a 32.99 21.78 36.49 注:SOAA酸味类氨基酸:Asp、Glu;SWAA甜味类氨基酸:Thr、Ala、Gly、Pro、Ser;BIAA苦味类氨基酸:Ile、Leu、Met、Phe、Trp、Val、His、Arg;同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 花生果仁中特殊功效氨基酸含量
Table 4 The content of special functional amino acids in peanut kernels
氨基酸 单位 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 CE g/100 g 4.12±0.10b 4.68±0.07a 4.21±0.12b 4.15±0.12b 4.59±0.15a MAA 19.44±0.91b 22.23±0.18a 20.46±0.42b 20.34±0.64b 22.10±0.40a FCAA 14.28±0.34b 16.01±0.06a 14.72±0.31b 14.68±0.42b 15.87±0.30a ABAA 3.63±0.06c 4.11±0.08a 3.86±0.10b 3.81±0.14b 4.10±0.07a PAAA 17.11±0.86c 19.76±0.16a 18.09±0.33b 18.08±0.54b 19.61±0.33a BCAA 3.95±0.12b 4.44±0.01a 4.05±0.10b 4.08±0.12b 4.33±0.05a AAA 3.14±0.09b 3.53±0.08a 3.26±0.08b 3.26±0.12b 3.45±0.08a CE/TAA % 14.96 14.88 14.55 14.36 14.78 MAA/TAA 70.60 70.64 70.72 70.32 71.13 FCAA/TAA 51.85 50.89 50.89 50.75 51.09 ABAA/TAA 13.17 13.05 13.35 13.19 13.24 PAAA/TAA 62.15 62.79 62.54 62.52 63.13 BCAA/AAA 125.93 125.76 124.11 125.38 125.29 BCAA/EAA 50.45 49.64 49.31 49.58 49.52 注:CE儿童必需氨基酸:His、Arg;MAA药用氨基酸:Asp、Glu、Gly、Met、Leu、Phe、Tyr、Lys、Arg;FCAA增香与着色氨基酸:Glu、Cys、Val、Leu、Lys、His、Arg;ABAA抗菌氨基酸:Phe、Trp、Gly;PAAA伯胺基氨基酸:Asp、Glu、Pro、Gly、Ala、Lys、Arg;BCAA支链氨基酸:Ile、Leu、Val;AAA芳香族氨基酸:Phe、Tyr、Trp。 表 5 花生果仁中必需氨基酸含量与鸡蛋蛋白、FAO/WHO标准模式的比较(mg/g N)
Table 5 The composition of essential amino acid in peanut kernels and comparison with egg’s protein and FAO/WHO standard model (mg/g N)
氨基酸 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 鸡蛋蛋白 FAO/WHO Ile 195 203 199 204 211 331 250 Leu 384 385 382 388 410 534 440 Lys 195 220 214 217 231 441 340 Met+Cys 96 94 109 103 107 386 220 Phe+Tyr 538 534 536 539 556 565 380 Thr 164 166 165 170 169 292 250 Trp 119 131 132 136 137 106 60 Val 248 248 248 254 248 411 310 TEAA 1937 1982 1986 2011 2069 3066 2250 E/T(%) 33.63 33.43 33.53 33.55 33.17 49.80 36.35 E/N(%) 50.67 50.21 50.44 50.49 49.64 99.22 57.11 表 6 花生仁中必需氨基酸营养价值评分
Table 6 Nutritional scores of essential amino acids in peanut kernels
品种 RC、
RCAAFAO/WHO Egg protein Ile Leu Lys Met+Cys Phe+Tyr Thr Trp Val SRC AAS* CS* P1 RC 0.78 0.87 0.57 0.44 1.41 0.66 1.98 0.80 45.70 24.93 39.46 RCAA 0.83 0.93 0.61 0.47 1.51 0.70 2.11 0.85 P2 RC 0.81 0.88 0.65 0.43 1.41 0.67 2.19 0.80 42.30 24.29 37.58 RCAA 0.83 0.90 0.66 0.44 1.44 0.68 2.24 0.82 P3 RC 0.80 0.87 0.63 0.50 1.41 0.66 2.20 0.80 42.93 28.29 43.67 RCAA 0.81 0.88 0.64 0.51 1.44 0.67 2.23 0.81 P4 RC 0.82 0.88 0.64 0.47 1.42 0.68 2.27 0.82 41.61 26.66 40.66 RCAA 0.82 0.88 0.64 0.47 1.42 0.68 2.27 0.82 P5 RC 0.85 0.93 0.68 0.49 1.46 0.68 2.29 0.80 42.58 27.74 41.10 RCAA 0.83 0.91 0.67 0.48 1.43 0.66 2.24 0.78 注:*表示第一限制氨基酸为Met+Cys。 -
[1] 付春, 张小军, 岳福良, 等. 特色花生新品系营养品质解析[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2017,22(5):32−38. [FU C, ZHANG X J, YUE F L, et al. Nutrition and quality analysis of special new peanut varieties[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University,2017,22(5):32−38. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2017.05.004 FU C, ZHANG X J, YUE F L, et al. Nutrition and quality analysis of special new peanut varieties[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017, 22(5): 32-38. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2017.05.004
[2] HASHIM I B, KOEHLER P E, EITENMILLER R R. Tocopherols in runner and Virginia peanut cultivars at various maturity stages[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society,1993,70(6):633−635. doi: 10.1007/BF02545333
[3] CAMPOS-MONDRAGÓN M G, CALDERÓN DE LA BARCA A M, DURÁN-PRADO A, et al. Nutritional composition of new peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars[J]. Grasas Y Aceites,2009,60(2):161−167. doi: 10.3989/gya.075008
[4] 颜孙安, 姚清华, 林香信, 等. 成熟度对‘红地球’葡萄氨基酸营养价值的影响[J]. 果树学报,2021,38(1):64−72. [YAN S A, YAO Q H, LIN X X, et al. Effects of maturity on amino acid nutrition of Red Globe Grape (Vitis vinifera L.)[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2021,38(1):64−72. doi: 10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20200167 YAN S A, YAO Q H, LIN X X, et al. Effects of maturity on amino acid nutrition of Red Globe Grape(Vitis vinifera L. )[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2021, 38(1): 64-72. doi: 10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20200167
[5] 万书波. 花生品种改良与高产优质栽培[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008 WANG S B. Peanut variety improvement and high yield and high quality cultivation[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2008.
[6] MARTÍNEZ -GIL A M, GARDE-CERDÁN T, LORENZO C, et al. Volatile compounds formation in alcoholic fermentation from grapes collected at 2 maturation stages: Influence of nitrogen compounds and grape variety[J]. Journal of Food Science,2012,71(1):71−79.
[7] SYAFUTRI M I, PRATAMA F, SYAIFUL F, et al. Effects of varieties and cooking methods on physical and chemical characteristics of cooked rice[J]. Rice Science,2016,23(5):282−286. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2016.08.006
[8] 孙娟娟, 阿拉木斯, 赵金梅, 等. 6个紫花苜蓿品种氨基酸组成分析及营养价值评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2019,52(13):2359−2367. [SUN J J, A L M S, ZHAO J M, et al. Analysis of amino acid composition and six native alfalfa cultivars[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2019,52(13):2359−2367. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.13.014 SUN J J, A L M S, ZHAO J M, et al. Analysis of amino acid composition and six native alfalfa cultivars[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(13): 2359-2367. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.13.014
[9] 赵凤敏, 李树君, 张小燕, 等. 不同品种马铃薯的氨基酸营养价值评价[J]. 中国粮油学报,2014,29(9):13−18. [ZHAO F M, LI S J, ZHANG X Y, et al. Nutritional evaluation of amino acids in different potato gultivars[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2014,29(9):13−18. ZHAO F M, LI S J, ZHANG X Y, et al. Nutritional evaluation of amino acids in different potato gultivars[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2014, 29(9): 13-18.
[10] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard. Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.124-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National food safety standard. Determination of amino acids in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[12] 朱圣陶, 吴坤. 蛋白质营养价值评价——氨基酸比值系数法[J]. 营养学报,1988,10(2):187−190. [ZHU S T, WU K. Evaluation of protein nutritional value-amino acid ratio coefficient method[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,1988,10(2):187−190. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.1988.02.015 ZHU S T, WU K. Evaluation of protein nutritional value-amino acid ratio coefficient method[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 1988, 10(2): 187-190. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.1988.02.015
[13] 颜孙安, 林香信, 钱爱萍, 等. 化学分析法的理想参考蛋白模式及其化学生物价研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2010,26(23):101−107. [YAN S A, LIN X X, QIAN A P, et al. The Study on the ideal reference protein model of chemical analysis and biological value[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2010,26(23):101−107. YAN SBA, LIN X X, QIAN A P, et al. The Study on the ideal reference protein model of chemical analysis and biological value[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(23): 101-107.
[14] 马庆华, 董辰希, 曹晗, 等. 3种野生大型真菌营养成分分析与评价[J]. 中国食用菌,2020,39(7):35−40. [MA Q H, DONG C X, CAO H, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional ingredients of three wild major fungi species[J]. Edible Fungi of China,2020,39(7):35−40. MA Q H, DONG C X, CAO H, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional ingredients of three wild major fungi species[J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2020, 39(7): 35-40.
[15] 杨月欣, 王光亚, 潘兴昌. 中国食物成分表(第一册)[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2017: 216−217 YANG Y X, WANG G Y, PAN X C. Chinese food composition table (Volume 1)[M]. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press, 2017: 216−217.
[16] 林茂, 赵景芳, 郑秀艳, 等. 不同种皮颜色花生生品的营养、感官和品质的分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2019,17(5):1647−1657. [LIN M, ZHAO J F, ZHENG X Y, et al. Analysis of nutrition, sense and quality of peanut seed with different testa color[J]. Mol Plant Breed,2019,17(5):1647−1657. doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.017.001647 LIN M, ZHAO J F, ZHENG X Y, et al. Analysis of nutrition, sense and quality of peanut seed with different testa color[J]. Mol Plant Breed, 2019, 17(5): 1647-1657. doi: 10.13271/j.mpb.017.001647
[17] 高桂琴, 赵雪娇, 仲昭欣, 等. 15 种坚果果仁氨基酸组成及含量差异分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(4):1173−1179. [GAO G Q, ZHAO X J, ZHONG Z X, et al. Analysis on the difference of amino acid composition and concentrations in 15 kinds of nut[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2020,11(4):1173−1179. GAO G Q, ZHAO X J, ZHONG Z X, et al. Analysis on the difference of amino acid composition and concentrations in 15 kinds of nut[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2020, 11(4): 1173-1179.
[18] 石太渊, 于淼, 韩艳秋. 辽宁花生品种营养成分及特性分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(22):142−147. [SHI T Y, YU M, HAN Y Q, et al. The nutrients and characteristic analysis of Liaoning peanut varieties[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(22):142−147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.22.029 SHI T Y, YU M, HAN Y Q, et al. The nutrients and characteristic analysis of Liaoning peanut varieties[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(22): 142-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.22.029
[19] 蒋莹. 氨基酸的应用[M]. 北京: 世界图书出版公司北京公司, 1996: 1−147 JIANG Y. Application of amino acids[M]. Beijing: World Book Publishing Company, Beijing Company, 1996: 1−147.
[20] 刘培基, 崔文甲, 王文亮, 等. 食用菌风味物质及其在美拉德反应中的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(15):188−193. [LIU P J, CUI W J, WANG W L, et al. Research progress of edible fungi flavor substances and their application in maillard reaction[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(15):188−193. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.15.032 LIU P J, CUI W J, WANG W L, et al. Research progress of edible fungi flavor substances and their application in maillard reaction[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(15): 188-193. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.15.032
[21] 尹蓉, 张倩茹, 王贤萍, 等. 不同杏品种种仁氨基酸组成分析[J]. 山西农业科学,2017,45(7):1087−1090, 1095. [YIN R, ZHANG Q R, WANG X P, et al. Composition analysis of amino acid in kernel of different apricot varieties[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(7):1087−1090, 1095. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2017.07.11 YIN R, ZHANG Q R, WANG X P, et al. Composition analysis of amino acid in kernel of different apricot varieties[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(7): 1087-1090, 1095. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2017.07.11
[22] 王晓媛, 王彦兵, 陈玉芹, 等. 6 种石斛属植物氨基酸组成及营养价值评价[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2019,31:601−607. [WANG X Y, WANG Y B, CHEN Y Q, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional value evaluation of 6 species of Dendrobium[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019,31:601−607. WANG X Y, WANG Y B, CHEN Y Q, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional value evaluation of 6 species of Dendrobium[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2019, 31: 601-607.
[23] 常思佳, 宁雪, 王日明, 等. 日光温室栽培模式下不同种质来源人参单体皂苷及氨基酸对比分析[J]. 人参研究,2019(3):18−24. [CHANG S J, NING X, WANG R M, et al. Comparative analysis of monomeric saponins and amino acids of ginseng from different germplasm sources in solar greenhouse cultivation mode[J]. Ginseng Research,2019(3):18−24. CHANG S J, NING X, WANG R M, et al. Comparative analysis of monomeric saponins and amino acids of ginseng from different germplasm sources in solar greenhouse cultivation mode[J]. Ginseng Research, 2019, (3): 18-24.
[24] 周苏, 刘磊. 冬虫夏草中氨基酸含量分析[J]. 现代食品,2017(5):116−118. [ZHOU S, LIU L. Analysis of amino acids in Cordyceps sinensis[J]. Modern Food,2017(5):116−118. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2017.05.040 ZHOU S, LIU L. Analysis of Amino Acids in Cordyceps Sinensis[J]. Modern Food, 2017, (5): 116-118. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2017.05.040
[25] 吴有锋, 谭亮, 沈建伟, 等. 柴达木枸杞中17种氨基酸的测定与分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(1):281−286. [WU Y F, TAN L, SHEN J W, et al. Determination and analysis of 17 amino acids in Qaidam Chinese wolfberry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(1):281−286. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.01.048 WU Y F, TAN L, SHEN J W, et al. Determination and analysis of 17 amino acids in Qaidam Chinese wolfberry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(1): 281-286. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.01.048
[26] 吴莹莹, 鲍大鹏, 王瑞娟, 等. 6 种市售工厂化栽培金针菇的氨基酸组成及蛋白质营养评价[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(10):263−268. [WU Y Y, BAO D P, WANG R J, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional evaluation of proteins in six samples of cultivated flammulina velutipes[J]. Food Science,2018,39(10):263−268. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201810040 WU Y Y, BAO D P, WANG R J, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional evaluation of proteins in six samples of cultivated flammulina velutipes[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(10): 263-268. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201810040
[27] 李美凤, 刘娟汝, 陈艳, 等. 3个不同产地的松露氨基酸组成及营养价值评价[J]. 食品工业,2021,1:342−346. [LI M F, LIU J R, CHEN Y, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional quality evaluation of truffles from 3 different growing regions[J]. The Food Industry,2021,1:342−346. LI M F, LIU J R, CHEN Y, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional quality evaluation of truffles from 3 different growing regions[J]. The Food Industry, 2021, 1: 342-346.
计量
- 文章访问数: 178
- HTML全文浏览量: 62
- PDF下载量: 16





 下载:
下载:
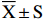
 下载:
下载: 